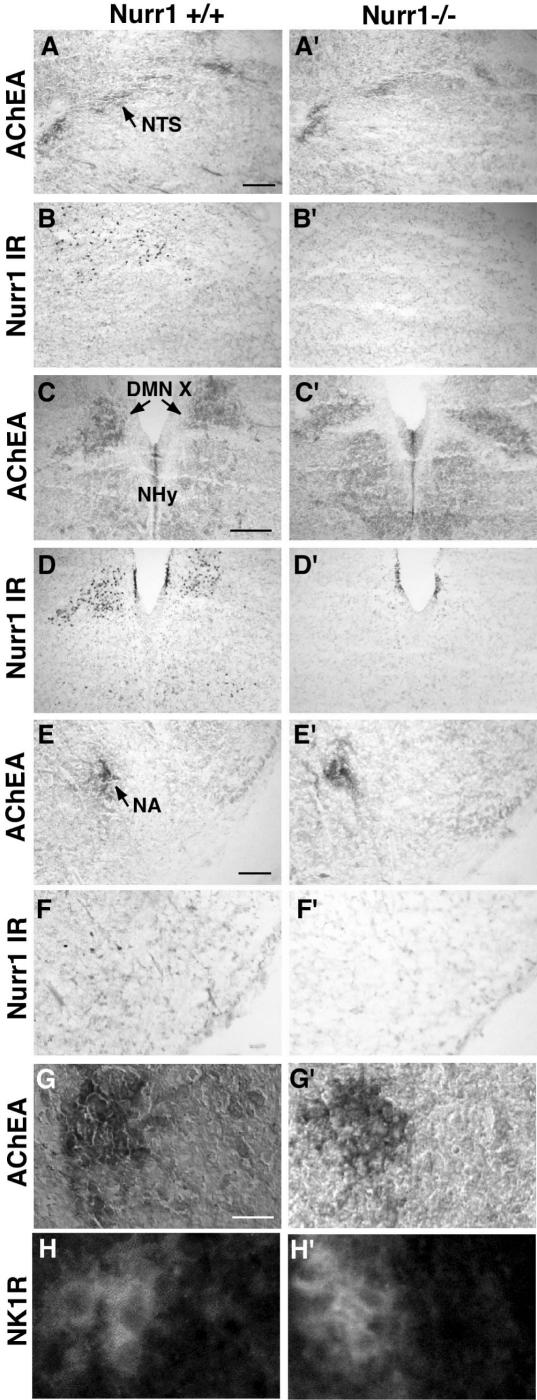
Figure 4. Ample Nurr1 expression in the brainstem of newborn pups.
A–F′, using an AChEA assay, the cholinergic neurones of the NTS (A), DMN X (C) and the nucleus ambiguous (E) in the dorsolateral, dorsomedial and ventrolateral medulla, respectively, were detected. Scattered Nurr1 immunoreactivity (IR) is evident in the area of the NTS (B) and nucleus ambiguous (F), and strong localized Nurr1 IR is detected in the DMN X (D). In Nurr1−/− pups, the AChEA assay reveals the presence of these cholinergic nuclei (A′, C′, E′), and, as expected, no staining is observed using the Nurr1 antibody (B′, D′, F′). Note the elongated shape of the DMN X in the Nurr1−/− DMN X (C′), which differs from that of the wild-type (C) (n= 4 wild-type and 4 Nurr1 knockout pups, see Results for quantification). G–H′, in the anterior part of the ventromedial medulla, the pre-Bötzinger complex can be visualized by IR for the substance P receptor, NK1R, within the area of the NA. In both wild-type and Nurr1 null mutant pups, AChEA assay shows the nucleus ambiguous (close-up of nucleus ambiguous in G and G′) and NK1R IR in the pre-Bötzinger (close-up in H and H′) areas. Nurr1 IR was not detected in the nuclei of the NK1R-expressing cells (not shown). The bars in A, C and E show 400 μm and in G 1500 μm.