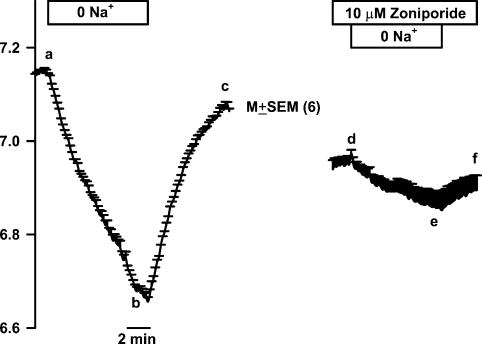
Figure 1. Effect of basolateral Na+ removal on TRC pHi.
A lingual epithelial preparation was perfused on both sides with control solution containing 150mm NaCl (RC; pH 7.4; Table 1). At the time period shown by the top horizontal bar the basolateral membrane solution was switched to a Na+-free solution (0 Na+) containing 150mm NMDG-Cl (R0Na; pH 7.4; Table 1). Under control conditions removal of Na+ decreased TRC pHi (a–b) and upon re-perfusing the control solution increased pHi to near its control value (b–c). In the second half of the experiment, the basolateral membrane was treated with 10μm zoniporide. In the presence of zoniporide, the changes in pHi upon removal (d–e) and re-addition (e–f) of Na+ were significantly attenuated. The pHi values are presented as mean±s.e.m. of n (number of ROIs within the taste bud).