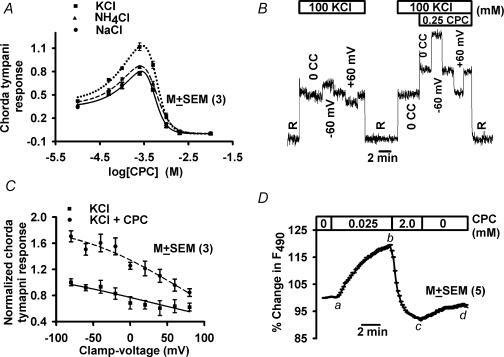
Figure 6. Cation selectivity and voltage sensitivity of the amiloride-insensitive channel.
A, CPC induced biphasic changes in rat chorda tympani responses to 100 mm NaCl + 5 μm Bz (•), 100 mm NH4Cl (▴), and 100 mm KCl (▪). The CPC-sensitive chorda tympani responses to KCl and NH4Cl were obtained by subtracting the maximum suppression value at 10 mm CPC. Each point represents the mean ± s.e.m. of the normalized chorda tympani response from 3 animals. B, rat chorda tympani responses to 100 mm KCl at zero current clamp (0cc), −60 mV and +60 mV voltage clamp in the absence (left trace) and presence (right trace) of 0.25 mm CPC. C, rat chorda tympani responses to 500 mm KCl between −80 and +80 mV lingual voltage clamp in the absence (▪) and presence of 0.25 mm CPC (•). Each point represents the mean ± s.e.m. of the normalized chorda tympani response from 3 animals. D, relative changes in [Na+]i in polarized rat fungiform taste receptor cells loaded with sodium green. The changes in [Na+]i are expressed as the percentage change in fluorescence intensity (F490) of sodium green. Values are presented as mean ± s.e.m. from 6 regions of interest within the taste bud.