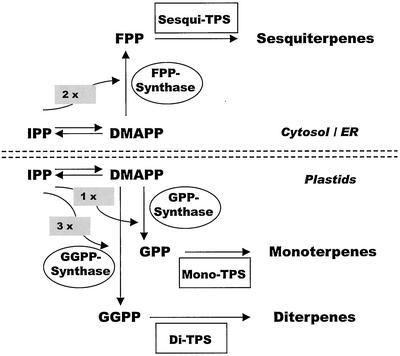
Figure 2.
Scheme of the pathways of terpenoid biosynthesis in conifers. The five-carbon precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), are formed via two pathways, the mevalonate pathway in the cytosol/endoplasmic reticulum and the 2-C-methylerythritol-4-phosphate pathway (via 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate) in plastids. Prenyltransferases (PTs) catalyze (1′-4) head-to-tail condensations of DMAPP with one, two, or three molecules of IPP to form geranyl diphosphate (GPP; GPP synthase), farnesyl diphosphate (FPP; FPP synthase), and geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP; GGPP synthase), respectively. Terpene synthases (TPS; cyclases) of three classes (mono-TPS, sesqui-TPS, and di-TPS) convert the three prenyl diphosphate intermediates into the hundreds of cyclic and acyclic terpenoids characteristic of conifers.