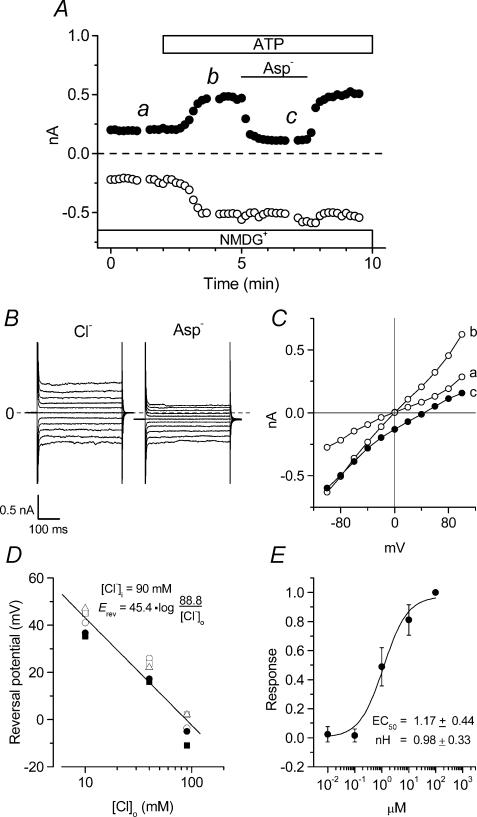
Figure 2. Anion sensitivity of extracellular ATP-induced membrane currents in mouse ventricular myocytes.
A, time course of extracellular ATP-induced whole-cell currents in NMDG-Cl solutions during application of 100 μm ATP to the bath. [Cl−]o was replaced to equimolar [Asp−]o during the period indicated by the bar. B, whole-cell current recordings at the time points b (Cl−) and c (Asp−) in A. C, I–V relationships of currents recorded at the time points indicated in A. D, reversal potential–log [Cl−]o relationships of whole-cell currents in the presence of extracellular ATP in 4 different cells in which [Cl−]o was changed from 90 to 10 mm in [NMDG+]-rich conditions. D, dose–response relationships of anion-sensitive [NMDG+ solutions] extracellular ATP-induced (difference) currents in 4 different cells. Responses were normalized to the maximum current density obtained at 100 μm ATP. The EC50 and nH coefficient correspond to the fitted curve.