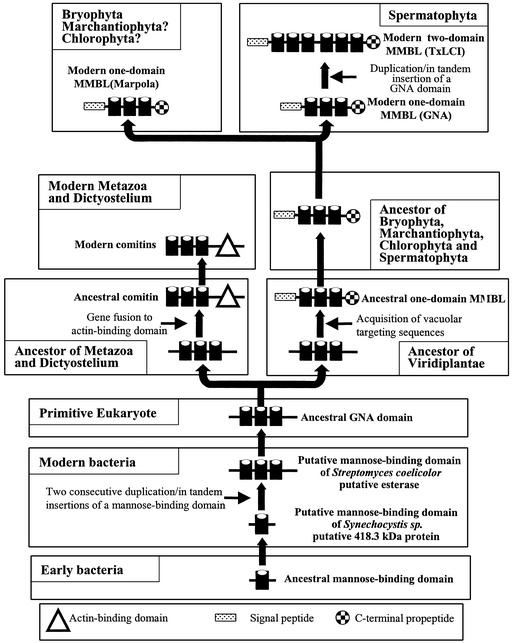
Figure 6.
Model of the molecular evolution of the superfamily of monocot Man-binding lectins. An ancestral prokaryotic Man-binding domain of approximately 40 amino acid residues evolved into a modern prokaryotic Man-binding domain that can be considered the ancestor of all modern GNA subdomains. Two consecutive duplication/in tandem insertions of this Man-binding domain gave rise to a prokaryotic domain equivalent to the modern GNA domain. In the ancestor of the modern metazoa and slime molds, the ancestral GNA domain fused to an actin binding to yield a comitin. Fusion of the ancestral GNA domain to vacuolar targeting sequences in an early ancestor of the Viridiplantae resulted in an extra-cytoplasmic protein similar to the modern one-domain monocot Man-binding lectins. This ancestral one-domain monocot Man-binding lectin served as the direct ancestor of all modern one-domain and two-domain monocot Man-binding lectins.