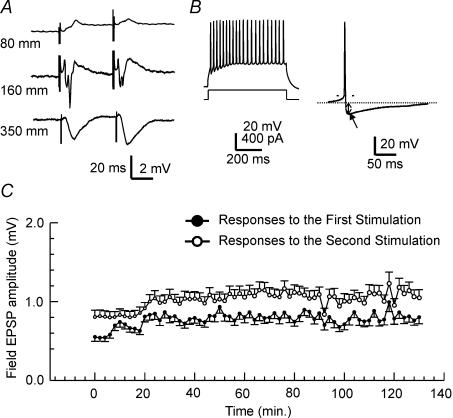
Figure 1. Evoked synaptic field responses and intracellular s.o. interneuronal responses to current injection in the whole hippocampus preparation.
A, evoked field potentials in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Field potentials were evoked by stimulating the Schaffer collateral pathway to elicit a maximal response. The numbers on the left represent the depth of recording electrode from the top of the IHP into the stratum oriens, the CA1 pyramidal layer, and below into the stratum radiatum. Note the polarity change at the CA1 pyramidal layer. B, left traces, tonic firing in s.o. interneurones. The top trace illustrates an s.o. interneurone firing tonically with little spike frequency adaptation. The lower trace is a schematic description of the depolarizing current intensity. Right trace, average of 5 APs of an s.o. interneurone. AP duration was taken at the baseline (indicated by the thin dotted line). The arrow indicates a large, fast AHP (fAHP). The amplitude of the fAHP was measured from the baseline to the maximal hyperpolarization. C, stable field responses to paired pulse stimulation. Maximal CA1 field potentials evoked by stimulating Schaffer collateral pathway were recorded at a depth of approximately 300 μm from the s.o. side of the hippocampus. The amplitude of the evoked field was measured from the maximal downward voltage deflection. Paired pulse stimuli were delivered every 30 s. The data are presented in the form of mean ±s.d. from 6 IHPs.