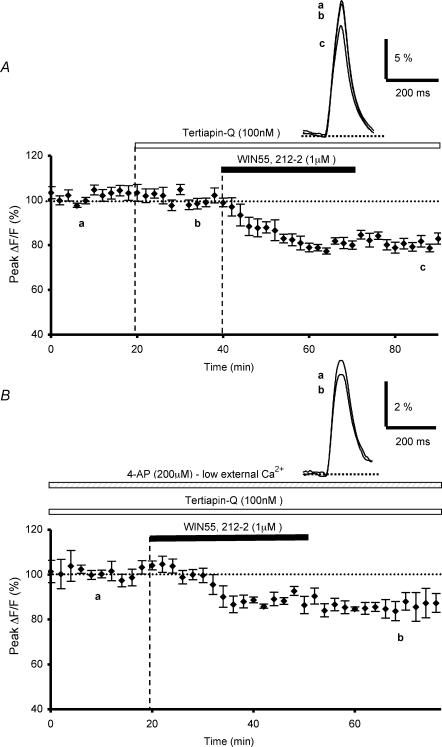
Figure 8. Effects of K+ channel blocker tertiapin-Q alone or combined with 4-APon WIN55,212-2-mediated inhibition of presynaptic calcium influx.
A, plot of normalized amplitudes of peak fluorescence transients before, during bath application of tertiapin Q (100 nm) and coapplication with WIN55,212-2 (1 μm), and after washout of WIN 55, 212-2 (n = 6). Note that this K+ channel blocker partially prevents the WIN55,212-2-induced inhibition of peak fluorescence transients. The inset represents superimposed averaged fluorescence changes in one of these experiments. B, plot of normalized amplitudes of peak fluorescence transients before, during and after application of WIN55,212-2 (1 μm), in the continuous presence of bath applied tertiapin-Q (100 nm) and 4-AP (200 μm) with a low extracellular calcium concentration (0.2 mm) (n = 4). Inset as in A. Note that in these conditions, tertiapin-Q and 4-AP drastically reduce the WIN55,212-2-induced inhibition of peak fluorescence transients.