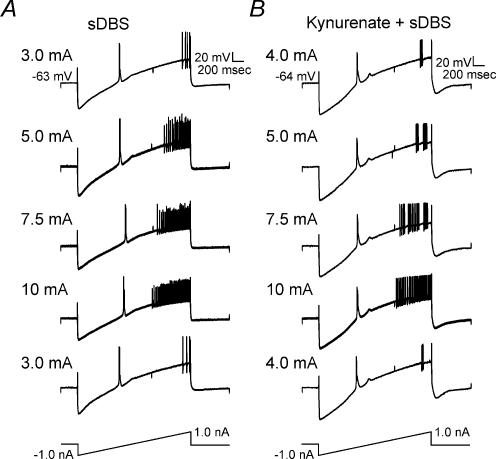
Figure 9. sDBS-induced increase in firing rate is dependent on stimulation strength, but independent of glutamate receptor activation.
A, sDBS was applied at different intensities in the same type 1 neurone while spike firing rate was evaluated using ramp current injection. Increasing sDBS current amplitude significantly increased the firing rate. Note that comparable responses to ramp current injection were elicited in both A and B when initial sDBS current intensities were retested after high currents (up to 10 mA) were used. This indicates that no adverse membrane effect resulted from high sDBS current levels. B, the same firing rate tests as inA was applied in another neurone where glutamatergic transmission was blocked with 2 mm kynurenate.