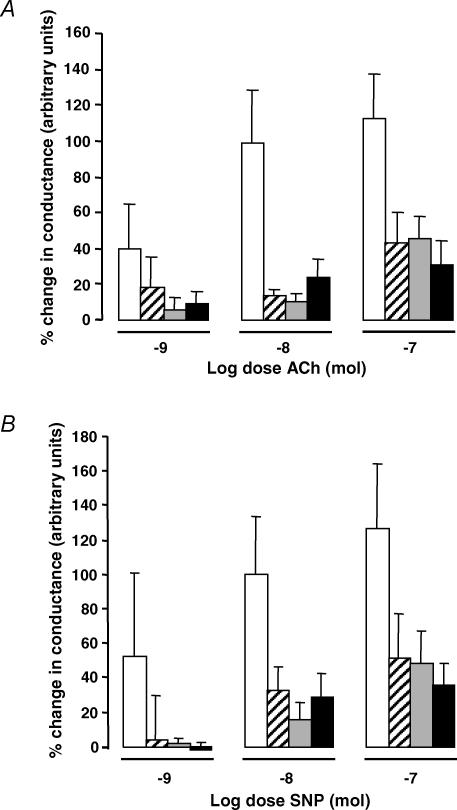
Figure 4. Vascular reactivity to ACh and SNP.
A, vascular reactivity to ACh in AIA rats. ACh induced a dose-dependent synovial vasodilatation (P = 0.009, two-way ANOVA), which was significantly attenuated in the vehicle (hatched columns; P < 0.002, Bonferroni post hoc), indomethacin (grey columns; P < 0.0001, Bonferroni post hoc) or SC-236-treated (filled columns; P < 0.0001, Bonferroni post hoc) AIA groups compared with the non-inflamed controls (open columns). There was no significant difference between the three AIA-treated groups. Data presented as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5–10). B, vascular reactivity to SNP in AIA rats. SNP induced a dose-dependent synovial vasodilatation (P = 0.013, two-way ANOVA) which was significantly attenuated in the vehicle (hatched columns; P = 0.013, Bonferroni post hoc), indomethacin (grey columns; P = 0.0045, Bonferroni post hoc) or SC-236-treated (filled columns; P = 0.0002; Bonferroni post hoc) AIA groups compared with the non-inflamed controls (open columns). There was no significant difference between the three AIA-treated groups. Data presented as mean ±s.e.m. (n = 5–6).