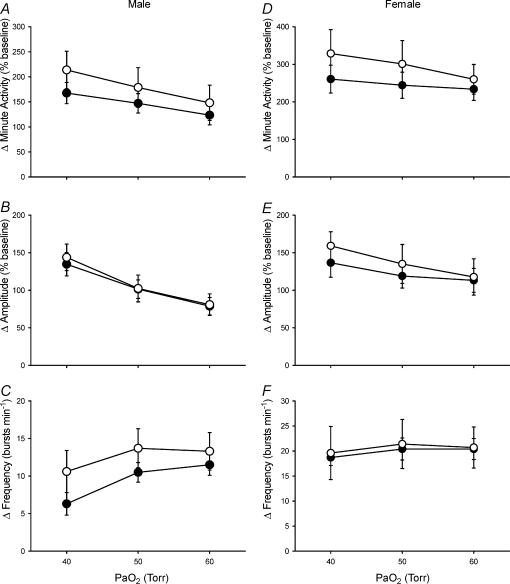
Figure 4. Hypoxic phrenic responses in anaesthetized and vagotomized male (A–C) and female (D–F) rats.
The increases in phrenic minute activity, burst amplitude and burst frequency (normalized to baseline; mean ±s.e.m.) in response to three levels of isocapnic hypoxia (arterial PO2 (PaO2) = 40, 50 and 60 Torr) are shown for adult rats raised in hypoxia for the first postnatal week (neonatal hypoxia (○): n = 11 males, 4 females) or in room air (control (•): n = 11 males, 5 females). No significant differences were detected between neontatal hypoxia and control rats (all P > 0.05).