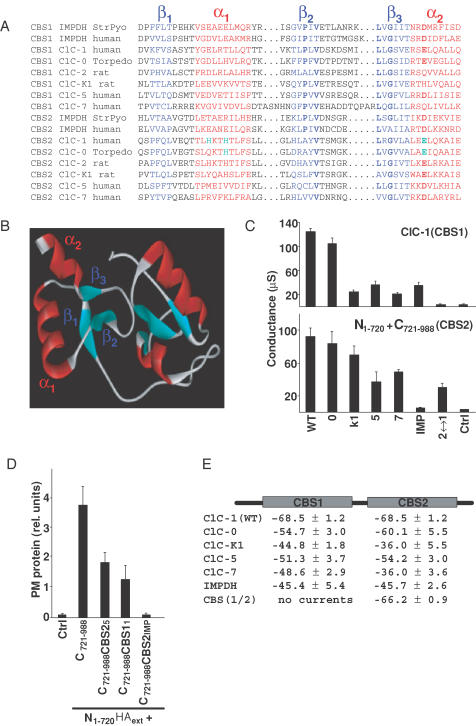
Figure 4. Functional conservation of CBS domains.
A, alignment of CBS domains (CBS1, CBS2) from the various CLC channels used in this study with those from human and bacterial IMPDH. The 3-D structure of the dimer of CBS domains of the bacteria S. pyogenes (StrPyo) has been solved by crystallography (Zhang et al. 1999). A more extensive alignment of CBS domains from different proteins is available on the internet (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de). Structural elements are highlighted by colours (β-strands in blue, α-helices in red), while bold characters indicate some of the residues that are conserved between CBS domains. Green indicates amino acids that drastically changed gating when mutated. have been studied by mutagenesis. B, homology model of the dimer of CBS domains from ClC-1. For modelling purposes, the region between CBS domains was replaced by that of S. pyogenes IMPDH. C, conductances (at 0 mV, in μS) of ClC-1 chimeras in which either the CBS1 domain was exchanged in the otherwise intact channel protein (upper panel), or in which CBS2 was exchanged in C721–988 to analyse split channels (lower panel). The proteins from which these CBS domains were taken are indicated below (0, ClC-0; K1, ClC-K1, etc.; IMP, human inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase; 2↔1 indicates that CBS2 was replaced by CBS1 (lower panel), or that CBS1 was replaced by CBS2 (upper panel). The figure represents an independent experiment with n = 6 oocytes. Another independent experiment gave similar results. D, surface expression of N1–720 tagged with an extracellular HA epitope in the presence of different C721–988 constructs in which the CBS2 domain of ClC-1 has been replaced by the indicated CBS2 domains, determined as in Fig. 1B. E, voltage values of half-activation for chimeras replacing CBS1 by CBS1 of the indicated proteins in ClC-1 and CBS2 by CBS2 of the indicated proteins in C721–988. Values were determined using a tail current analysis protocol, as described in Methods with two batches of oocytes, each batch containing n = 6 oocytes.