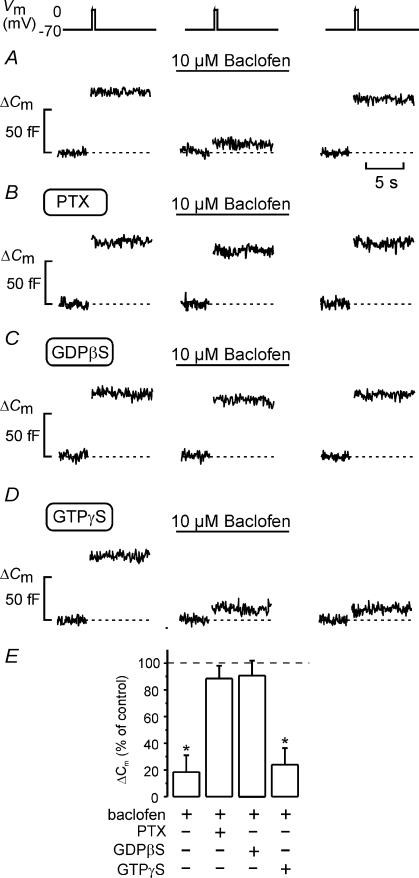
Figure 5. Baclofen-induced inhibition of exocytosis is mediated by activation of a Gi/o protein.
A–E, effects of 10 μm baclofen on exocytosis (ΔCm) elicited by 500 ms voltage-clamp depolarizations of the membrane potential (Vm) from −70 to 0 mV applying the standard whole-cell configuration to rat β-cells. Changes in cell capacitance were measured before and 2 min after the addition of baclofen, and 4 min after wash-out of the agonist under control conditions (A), in cells treated for > 20 h with 100 ng ml−1 pertussis toxin (PTX; B), with 0.5 mm GDPβS included in the pipette solution (C) and in the presence of 0.1 mm intracellular GTPγS (D). Cyclic AMP (0.1 mm) was included in all pipette solutions. E, histogram showing changes in cell capacitance (ΔCm) normalized to the respective controls (before addition of baclofen). Data are the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5–6 cells; *P < 0.01).