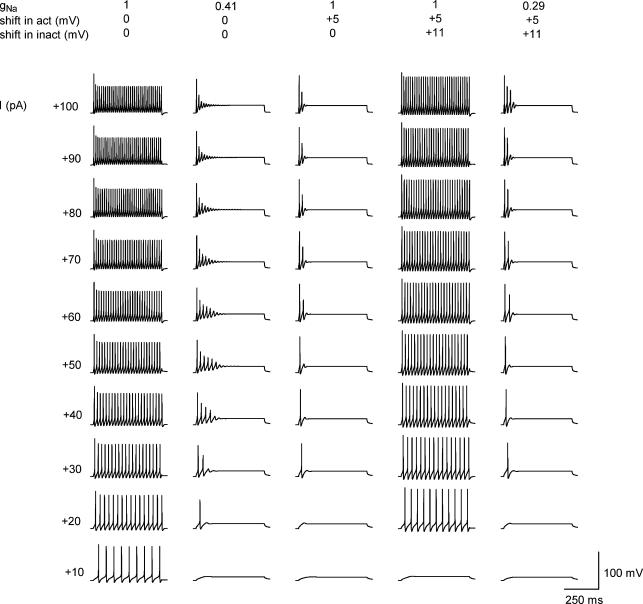
Figure 7. Computer simulation of firing adaptation in SG neurone.
A basic model of TFN from Melnick et al. (2004). Repetitive firing evoked by 500 ms current pulses of increasing intensity in a basic model (1/0/0). Reduction of Na+ conductance (gNa) in the axon initial segment to 0.41 induced firing adaptation (0.41/0/0). An activation shift by +5 mV, without lowering gNa, resulted in a strong firing adaptation (1/+5/0). A +11 mV shift in inactivation characteristics restored tonic firing in a model with control gNa (1/+5/+11). Reduction in gNa to 0.29 induced spike frequency adaptation in a model with shifted activation and inactivation characteristics (0.29/+5/+11). The resting potential was −70 mV in all simulations.