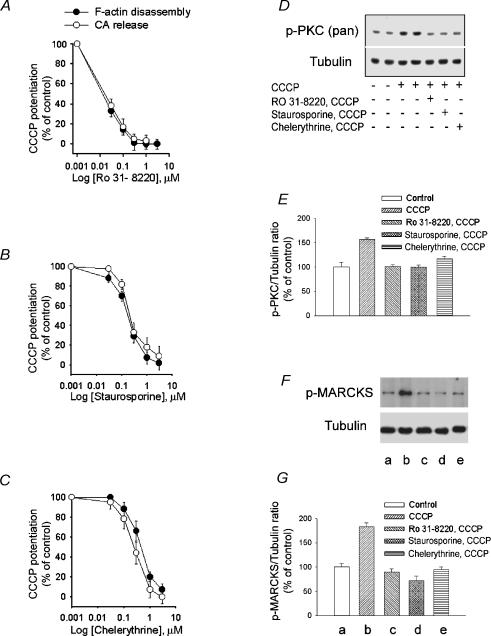
Figure 6. Effects of PCK inhibitors on the potentiation by CCCP of cortical F-actin disassembly, catecholamine secretion and PKC and MARCKS phosphorylation.
A–C, CCCP potentiation of high K+ depolarization-induced F-actin disassembly and catecholamine release was inhibited by RO31-8220, staurosporine and chelerythrine in a concentration-dependent manner. D, Western blot analysis of extracts from CCCP-treated bovine chromaffin cells in the presence or absence of PKC inhibitors. Chromaffin cells were pre-exposed to a Krebs-Hepes solution (control) or to the same solution containing either 1 μm of each of the PKC inhibitors RO31-8220, staurosporine or chelerythrine during 8.5 min. This was followed by incubation with Hepes solution (control) or 2 μm CCCP in Hepes solution for 90 s. The reaction was stopped by addition of ‘Sample buffer’ as described in Methods. Proteins in whole cell lysates were detected by Western blotting with phospho-PKC (pan), and tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as the gel-loading control. E, PKC phosphorylation expressed as percentage increase in phospho-PKC content relative to unstimulated (control) cells. Bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of data obtained from 3 different experiments. *P < 0.01 versus control. F, CCCP-induced phosphorylation of MARCKS. Chromaffin cells were incubated for 90 s with either Krebs-Hepes solution or the solution containing 2 μm CCCP. Cell extracts were prepared and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting with phospho-MARCKS and tubulin antibodies. Tubulin was used as the gel-loading control. The effect of PKC inhibitors on CCCP-induced MARCKS phosphorylation is also shown. G, MARCKS phosphorylation expressed as percentage increase in phospho-MARCKS content relative to un-stimulated (control) cells. Letters a to e below the bars correspond to the equivalently labelled lanes in F. Bars represent mean ± s.e.m. of data obtained from 8 different experiments. *P < 0.01 versus control.