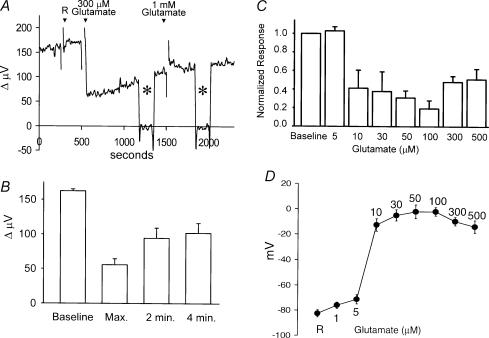
Figure 5. Glutamate-induced alterations in H+ flux.
A, responses obtained from a single horizontal cell. Application of 1 ml Ringer solution (R) did not alter measured H+ flux. A subsequent 1 ml application of the same solution containing glutamate (final concentration, 300 μm) produced a sharp decrease in H+ flux, which partially recovered with time. The electrode was moved, as indicated by the asterisks, to a background position 250 μm away from the cell. Addition of 1 mm glutamate to the bath had no additional effect. B, average responses to 300 μm glutamate obtained from eight cells showing the maximum alteration just after the application of glutamate and the response obtained 2 and 4 min later. C, dose-dependence of glutamate-induced alterations in measured H+ flux. Each bar is indicative of the response of six cells. Each cell was exposed to only one glutamate concentration. Values have been normalized to the responses obtained just prior to the application of glutamate. D, voltage changes induced by glutamate recorded in six separate horizontal cells obtained using sharp microelectrodes.