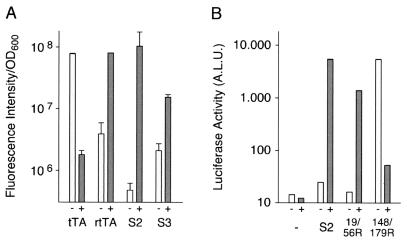
Figure 1.
Dox-dependent gene activation by novel rtTA alleles. (A) rtTA-mediated expression of GFP+ in yeast cells transformed with plasmid pCM190-GFP+ carrying the coding sequence of tTA, rtTA, or rtTA-S2 and -S3, the newly identified alleles, respectively, were grown overnight in the absence or the presence of 10 μg/ml Dox. Suspensions of yeast cells at an OD600 of 2 were exited at 490 nm, and fluorescence emission was measured at 512 nm. (B) Characterization of rtTA-S2 and its derivatives. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmid pUHC13-3 carrying the luciferase gene under Ptet-1 control and plasmids containing the coding sequence of transactivators rtTA-S2, -19/56R, or -148/179R, respectively. Cells were grown in the absence or in the presence of 5 μg/ml Dox. After 24 h, luciferase activity from the cell extracts was determined. Values shown are arbitrary light units.