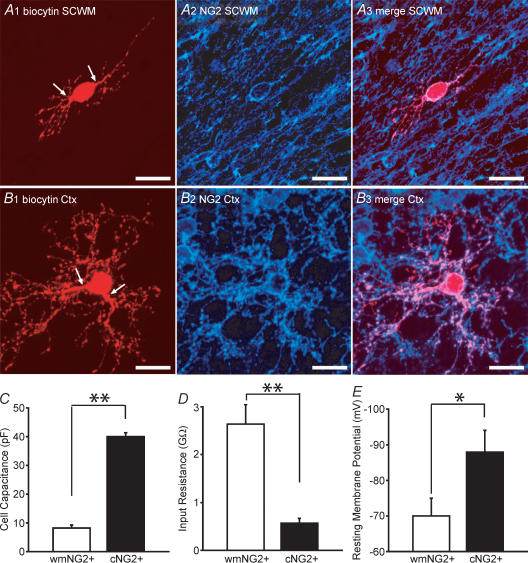
Figure 2. Distinct morphology and membrane properties of white matter NG2+ and cortical NG2+ cells.
A1, a low fluorescence intensity white matter (wm) EGFP+ cell after biocytin injection, followed by rhodamine conjugation. The cell has a bipolar morphology (arrows indicate processes). A2–A3, this cell was NG2+ and was morphologically representative of the EGFP+/white matter NG2+ cells identified. B1, cortical EGFP+ cell processed with the same protocol as in A1. Although the cell body is a similar size to the white matter NG2+, a distinct arborization of processes is apparent. B2–B3, this cell was also found to be NG2+. C and D, measurement of whole-cell capacitances, input resistances in white matter NG2+ (open bars; n = 28) and cortical NG2+ cells (filled bars; n = 40). E, resting membrane potential in white mater NG2+ (open bars; n = 7) and cortical NG2+ cells (filled bars; n = 10). Scale bars, 20 μm. All data was obtained from P5–P8 CNP-EGFP mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 Mann-Whitney U test.