Figure 4.
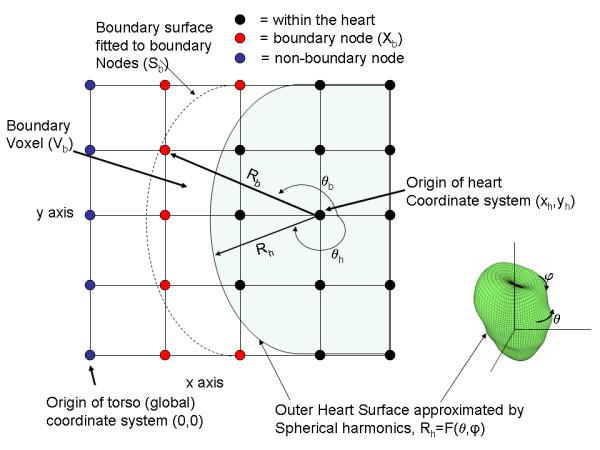
Finding boundary nodes and creating the boundary surface. A convenient origin within the heart serves as the basis for fitting a spherical harmonic expansion to the outer heart surface, which generates a surface characterized by the radius Rh(θ,Φ). Voxels that have nodes both within and without of this surface are boundary voxels. Within these voxels, the nodes outside of the heart are boundary nodes (red). A surface ("boundary surface") is fitted to these nodes by performing another spherical harmonic expansion about the heart origin. This surface is characterized by the radius Rb(θ,Φ).
