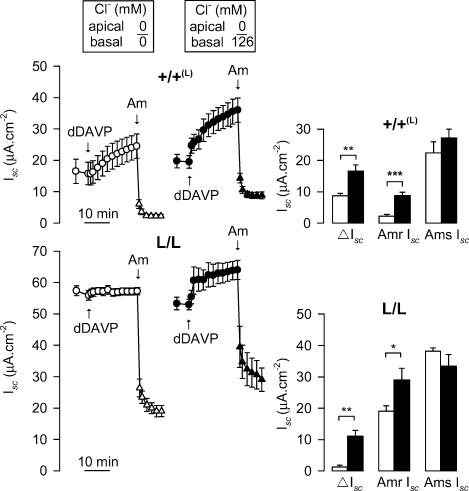
Figure 5. Effects of apical and basal substitution of Cl− on the Isc elicited by dDAVP in wild-type and Scnn1b mutant L/L CCD cells.
Sets of confluent +/+(L) (upper graphs) and L/L (lower graphs) CCD cells were incubated with apically and basally Cl− substituted (Cl−, 0 mm) solutions (^) or with apical Cl−-substituted solution and basal HFM (Cl−, 126 mm) (•) as described in Methods. After equilibrating the traces, Isc was measured before and after sequential additions of basal dDAVP (10−8m) and apical amiloride (10−5m). δIsc represents the relative increase in Isc induced by dDAVP. Amr Isc and Ams Isc represent the amiloride-resistant and -sensitive components, respectively, of Isc measured in cells incubated with apical and basal Cl−-substituted solutions (open bars) or apical Cl−-substituted solution and basal HFM (filled bars). Values are means ± s.e.m. from five separate experiments for each condition tested. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 between groups.