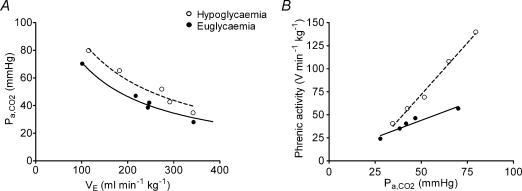
Figure 4. The effect of  upon Pa,CO2 and the effect of ΔPaCO2 upon phrenic nerve activity; increased metabolism and CO2 chemosensitivity during hypoglycaemia.
upon Pa,CO2 and the effect of ΔPaCO2 upon phrenic nerve activity; increased metabolism and CO2 chemosensitivity during hypoglycaemia.
A, representative data taken from a single experiment. Steady-state Pa,CO2 is sampled at various levels of artificial 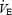 measured as integrated tracheal airflow during euglycaemia (•) and hypoglycaemia (○). Data are shown fitted by hyperbolic functions:
measured as integrated tracheal airflow during euglycaemia (•) and hypoglycaemia (○). Data are shown fitted by hyperbolic functions: 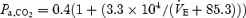 and
and 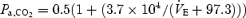 during euglycaemia (r2= 0.98) and hypoglycaemia (r2= 0.95), respectively. During insulin-induced hypoglycaemia, there was an upward shift in the position of the
during euglycaemia (r2= 0.98) and hypoglycaemia (r2= 0.95), respectively. During insulin-induced hypoglycaemia, there was an upward shift in the position of the 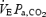 curves. B, representative raw data from the same animal. Phrenic minute activity is measured at the same steady-state levels of Pa,CO2 shown in A. Data are shown fitted by linear regression: phrenic minute activity = 0.75Pa,CO2+ 6.6 and phrenic minute activity = 2.24Pa,CO2− 39.9 during euglycaemia (r2= 0.92) and hypoglycaemia (r2= 0.99), respectively. Linear regression showed an increase of phrenic CO2 sensitivity during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia.
curves. B, representative raw data from the same animal. Phrenic minute activity is measured at the same steady-state levels of Pa,CO2 shown in A. Data are shown fitted by linear regression: phrenic minute activity = 0.75Pa,CO2+ 6.6 and phrenic minute activity = 2.24Pa,CO2− 39.9 during euglycaemia (r2= 0.92) and hypoglycaemia (r2= 0.99), respectively. Linear regression showed an increase of phrenic CO2 sensitivity during insulin-induced hypoglycaemia.