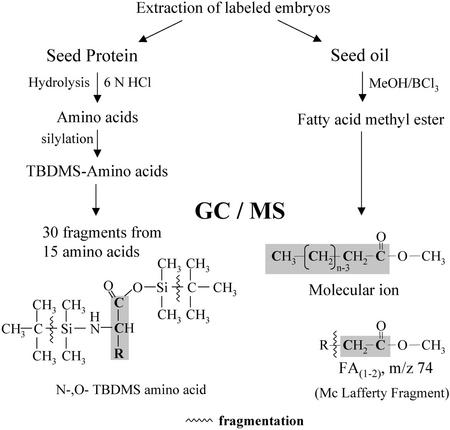
Figure 1.
Overview of the analytical techniques used for the measurement of 13C labeling in amino acids and fatty acids (see also “Materials and Methods”). After extraction of labeled embryos, the seed protein was hydrolyzed and the amino acids derivatized to their N,O-t-butyl-dimethylsilyl (TBDMS) derivatives. By GC/MS, the amino acid molecule is represented by the fragment M-57. For most amino acids, additional fragments were measured that represent parts of the amino acid molecule. The abundances of mass isotope isomers (isotopomers) of a measured fragment (m0, m1, m2… mn) were corrected for isotopomer content in the derivatization reagent and for heteroatoms (1H, 13C, 15N, 17O, 18O, 29Si, and 30Si) as well as for natural 13C in the derivatized molecule fragment. Finally, the relative abundance of mass isotopomers (13C1, 13C2, 13C3… 13Cn) was obtained. After transmethylation of seed oil, fatty acid methyl esters were analyzed by GC/MS. The molecular ion and the McLafferty fragment (m/z 74) were measured and the relative abundance of mass isotopomers was obtained as described for the amino acids.