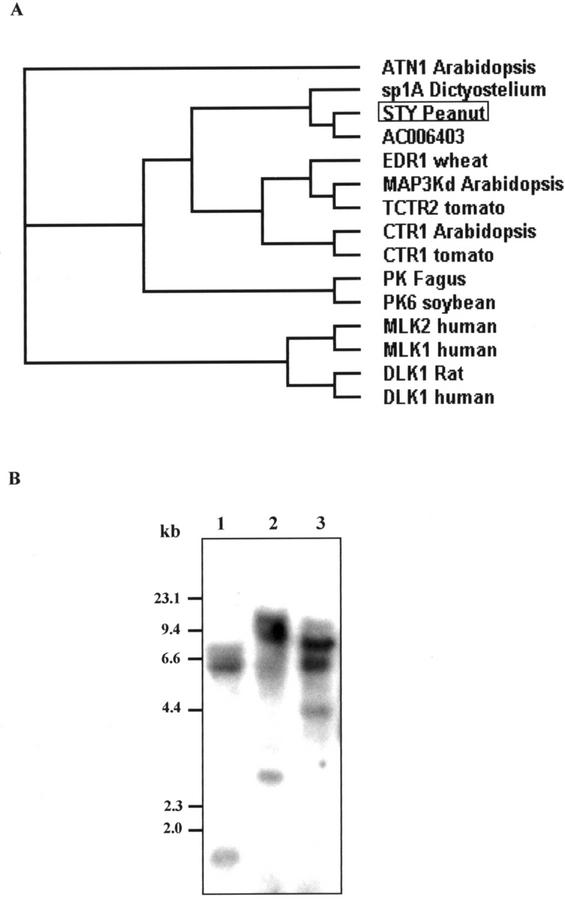
Figure 2.
A, Phylogenetic tree based on an alignment of peanut STY kinase (STY, accession no. AY027437) with putative protein kinase from Arabidopsis (accession no. AC006403) and 13 related proteins. GenBank accession numbers are: ATN 1 (Arabidopsis), S61766; sp1A (D. discoideum), P18160; EDR 1 (barley [Hordeum vulgare]), AAG31142; MAP3K (Arabidopsis), AA7459; TCTR2 (Lycopersicum esculentum), T06576; CTR1 (Arabidopsis), Q05609; CTR1 (L. esculentum), AAD10057; K (Fagus sylvatica), CAA66149; PK6 (soybean), S29851; MLK1 (human), P80192; MLK2 (human), Q02779; DLK (Rattus norvegicus), JC53399; and DLK (human), NP 00472. Protein sequences were aligned using the ClustalW. Distance trees were calculated using the neighbor-joining method. The lengths of the branches are proportional to the degree of divergence and thus correspond to the statistical significance of the phylogeny between the protein sequences. B, Southern-blot analysis STY kinase. Genomic DNA (20 μg) from immature peanut seed was digested with EcoRI (lane 1), SacI (lane 2), and BamHI (lane 3), separated on 0.8% (w/v) agarose gel, and probed with full-length STY kinase cDNA at high-stringency conditions (hybridization at 65°C, and washes at 65°C and 0.1× SSC).