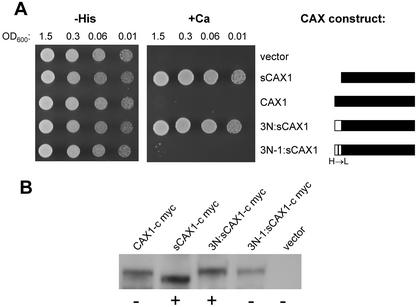
Figure 5.
A, Suppression of Ca2+ sensitivity of the pmc1 vcx1 cnb1 yeast mutant (K667) by sCAX1 with N-terminal fusions of either the wild-type NRR of CAX3 (3N:sCAX1) or the NRR of CAX3 containing a His to Leu single amino acid change (3N-1:sCAX1). The CAX constructs are depicted as bars: A black bar represents portions of the CAX1 open reading frame and a white bar represents portions of the CAX3 open reading frame (not to scale). The same assay conditions were used as described in Figure 2, except yeast growth is shown after 2 d. A representative experiment is shown. B, Western blot showing relative levels of the various CAX constructs used in the suppression assay. Equal amounts of total protein isolated from yeast strains expressing each c-myc-tagged construct as indicated were separated by SDS-PAGE, blotted, then subjected to western-blot analysis using an anti-c-myc monoclonal antibody. The ± signs designate whether the CAX construct was able to suppress the yeast vacuolar transport mutant, as shown in A.