Abstract
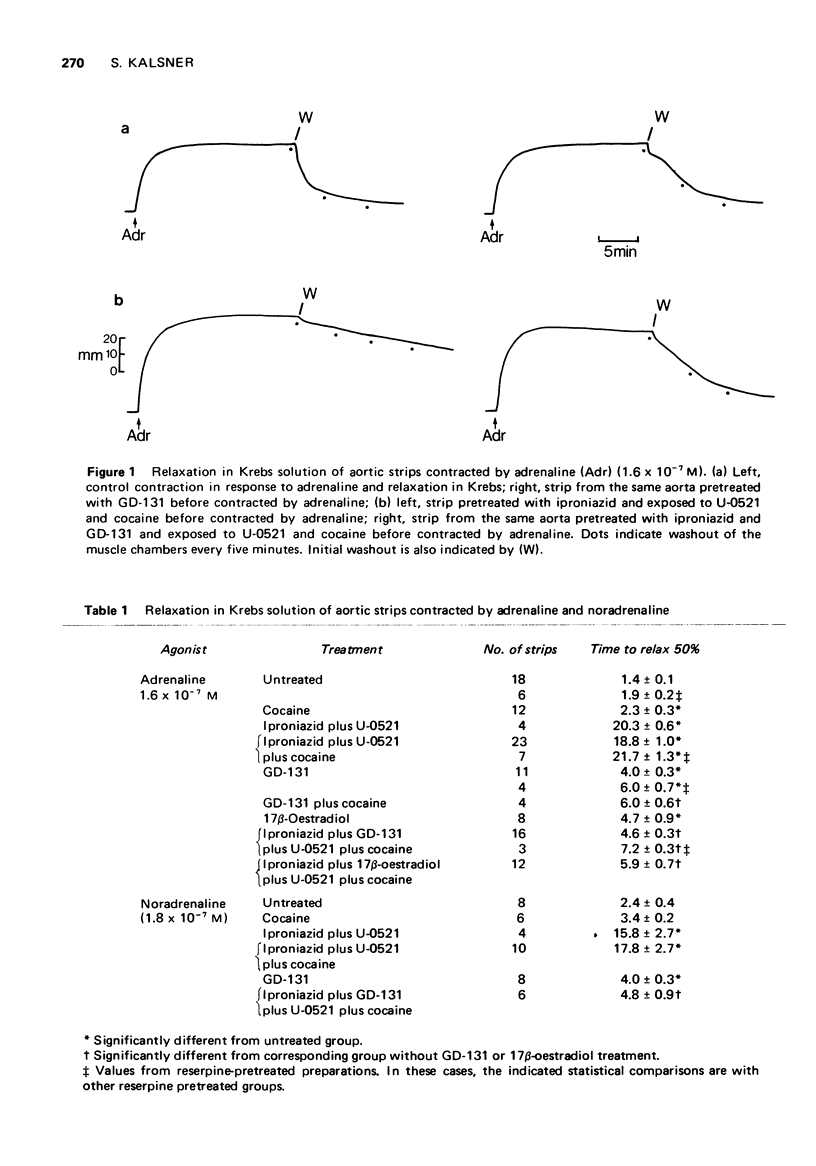
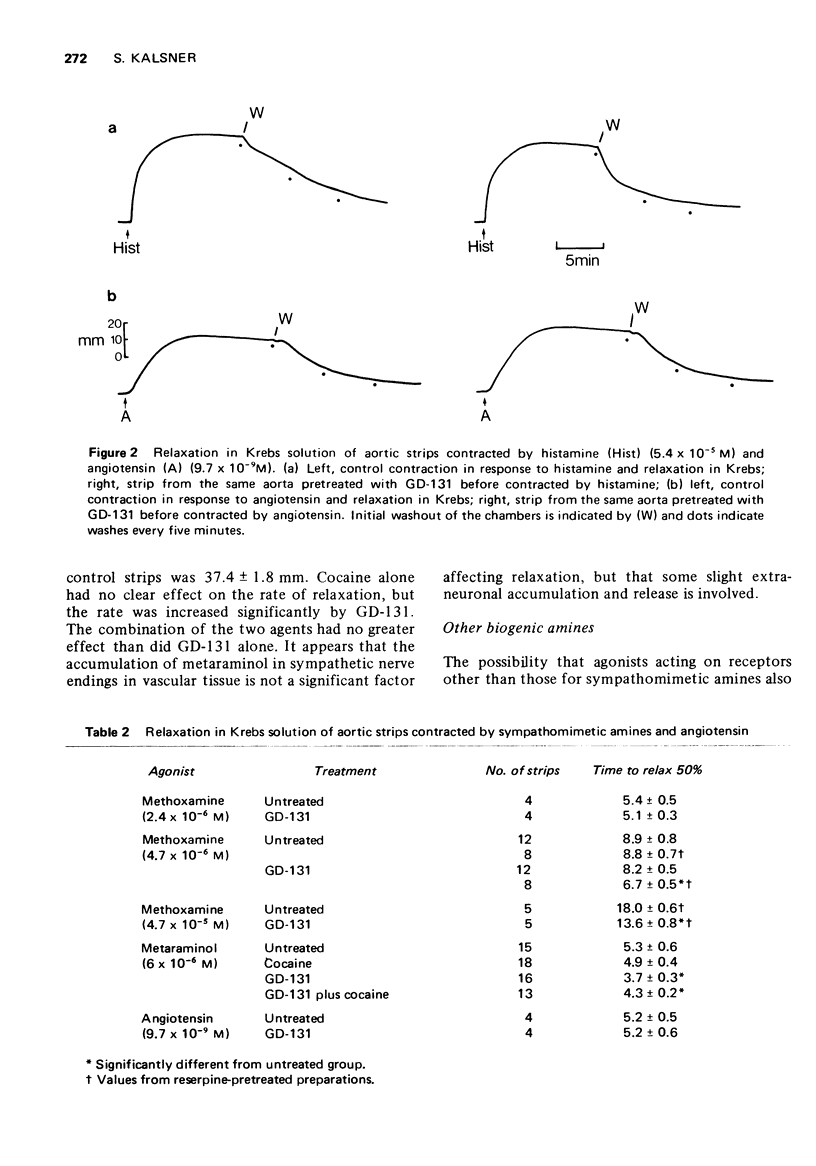
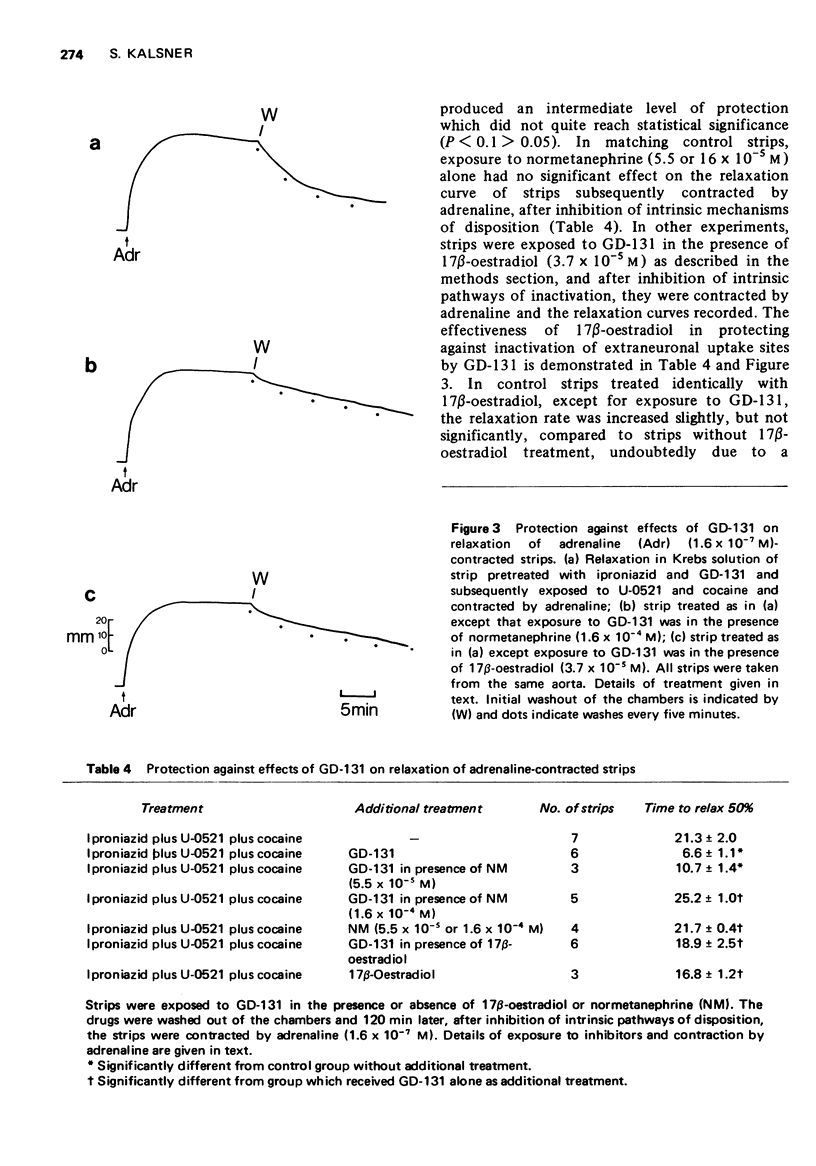
1 The role of the uptake and release of agonist from extraneuronal sites in the termination of responses of rabbit aortic strips to amines was studied. 2 Strips were contracted with adrenaline or noradrenaline and after response plateau was reached, the muscle chambers were washed free of agonist and the relaxation in Krebs solution recorded. After inhibition of catechol-O-methyl-transferase, monoamine oxidase and neuronal uptake the relaxation rate was greatly prolonged. Evidence is provided that this very slow relaxation resulted from the accumulation of intact amine at extraneuronal sites during exposure to the agonist and its subsequent release past receptors due to a reversal of the concentration gradient after washout. 3 Pretreatment with the haloalkylamine, GD-131 (N-cyclohexylmethyl-N-ethyl-beta-chloroethylamine), an inhibitor of extraneuronal uptake, returned the slow relaxation rate after enzyme inhibition towards that of control strips. By blocking the extraneuronal transport of amines their accumulation at intracellular loci after enzyme inhibition was prevented. 4 The effects of GD-131 and 17beta-oestradiol on the relaxation rate of untreated strips contracted by adrenaline and noradrenaline confirmed that extraneuronal uptake to sites of enzymatic activity is the major mechanism terminating their action. 5 Inactivation of extraneuronal transport sites by GD-131 was prevented by protecting them with 17beta-oestradiol or normetanephrine during exposure to the haloalkylamine, pointing to a common site of action of these agents on a specific carrier system for amines. 6 Evidence is presented that the relaxation from contractions induced by histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine also involves extraneuronal accumulation and release, probably by an uptake process which is identical to the one for catecholamines.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avakian O. V., Gillespie J. S. Uptake of noradrenaline by adrenergic nerves, smooth muscle and connective tissue in isolated perfused arteries and its correlation with the vasoconstrictor response. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):168–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., McCulloch M. W., Story D. F., Wright M. E. Factors affecting the extraneuronal inactivation of noradrenaline in cardiac and smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Oct;46(2):243–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb06869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Hamilton D. N., Hosie J. A. The extraneuronal uptake and localization of noradrenaline in the cat spleen and the effect on this of some drugs, of cold and of denervation. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):563–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Muir T. C. Species and tissue variation in extraneuronal and neuronal accumulation of noradrenaline. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;206(3):591–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie J. S., Towart R. Uptake kinetics and ion requirements for extraneuronal uptake of noradrenaline by arterial smooth muscle and collagen. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;47(3):556–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Effects of tyramine on responses to and inactivation of histamine in aortic strips. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Nov;175(2):489–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Mechanism of hydrocortisone potentiation of responses to epinephrine and norepinephrine in rabbit aorta. Circ Res. 1969 Mar;24(3):383–395. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.3.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Nickerson M. A method for the study of mechanisms of drug disposition in smooth muscle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;46(5):719–730. doi: 10.1139/y68-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Nickerson M. Disposition of norepinephrine and epinephrine in vascular tissue, determined by the technique of oil immersion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Feb;165(2):152–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Nickerson M. Disposition of phenylephrine in vascular tissue, determined by the oil-immersion technique. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Sep;163(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Nickerson M. Effects of a haloalkylamine on responses to and disposition of sympathomimetic amines. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;35(3):440–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S., Nickerson M. Effects of reserpine on the disposition of sympathomimetic amines in vascular tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;35(3):394–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Potentiation of responses to histamine in aortic strips by steroids. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;48(7):443–449. doi: 10.1139/y70-068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Steroid potentiation of responses to sympathomimetic amines in aortic strips. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;36(3):582–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt P. J. Inhibition of noradrenaline uptake 2 in the isolated rat heart by steroids, clonidine and methoxylated phenylethylamines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Dec;20(3):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


