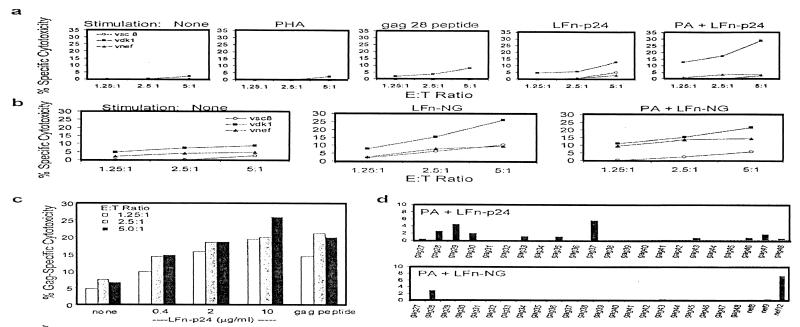
Figure 3.
LFn-p24 and LFn-NG induce human HIV-specific CTL in an in vitro vaccination assay. Adherent PBMC from asymptomatic HIV-infected donor 606 (a–d) were activated with GM-CSF and treated for 2 h with nothing, PHA, HIV immunodominant peptide, or LFn-p24 or LFn-NG in the presence or absence of PA, before adding autologous PBMC. Ten to fourteen days later, the induction of a secondary CD8 T cell response was measured by 51Cr-release assay against autologous B cell lines infected with recombinant vv expressing gag (vdk1), nef (vnef), or lacZ control (vsc8). (a) LFn-p24 induces gag-specific CTL from donor 606 as much as the immunodominant peptide, gag 28. However, the response is greatly enhanced by PA delivery of the antigen. (b) LFn-NG when added with PA stimulates both gag- and nef-specific CTL activity from the same donor. (c) The induction of gag-specific CTL by LFn-p24 is dose-dependent in the presence of a fixed amount of PA (10 μg/ml). (d) CTL from subject 606 recognize immunodominant epitopes in gag28, nef 8, and nef 12. Stimulation of PBMC from donor 606 with LFn-p24 plus PA induces a response to the subdominant epitope gag37. Data from a 4-h assay performed at an E:T ratio of 5:1 are shown. The activities are presented as the percentage of HIV-1 gag-specific cytotoxicity.