TABLE 5.
Performance for models with nonuniform crossing over and uniform gene conversion with unphased data
| γa | ρa | g(γ)b | g(ρ)b | B(γ)c | B(ρ)c |
E(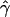 )d )d
|
E(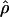 )d )d
|
V(γ)e | V(ρ)e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hudson's composite-likelihood method | |||||||||
| 20 | 20 | 0.420 | 0.972 | 0.780 | 0.509 | 12.499 | 20.320 | 0.986 | 0.448 |
| 60 | 20 | 0.592 | 0.958 | 0.763 | 0.413 | 39.479 | 22.390 | 0.668 | 0.533 |
| 80 | 20 | 0.636 | 0.948 | 0.776 | 0.418 | 59.159 | 22.102 | 0.611 | 0.535 |
| 20 | 40 | 0.288 | 0.964 | 0.841 | 0.654 | 9.440 | 37.000 | 1.047 | 0.360 |
| 40 | 40 | 0.384 | 0.984 | 0.853 | 0.578 | 18.940 | 39.720 | 0.856 | 0.356 |
| Summary statistics method | |||||||||
| 20 | 20 | 0.578 | 0.938 | 0.501 | 0.528 | 24.482 | 21.220 | 1.208 | 0.598 |
| 60 | 20 | 0.732 | 0.866 | 0.529 | 0.498 | 66.330 | 22.578 | 0.745 | 0.773 |
| 80 | 20 | 0.772 | 0.832 | 0.518 | 0.486 | 84.518 | 24.412 | 0.600 | 0.911 |
| 20 | 40 | 0.458 | 0.894 | 0.549 | 0.695 | 25.312 | 36.030 | 1.462 | 0.457 |
| 40 | 40 | 0.608 | 0.88 | 0.561 | 0.623 | 42.800 | 38.464 | 0.974 | 0.503 |
γ and ρ denote the true values of the gene-conversion and crossing-over rates under which 500 data sets were simulated.
g(γ) and g(ρ) denote the fraction of the data sets for which the estimates of gene conversion (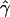 ) and crossing over (
) and crossing over (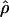 ) lie within a factor of 2 of the true values (i.e., γ and ρ), respectively.
) lie within a factor of 2 of the true values (i.e., γ and ρ), respectively.
B(γ) and B(ρ) denote the fraction of times the estimates of gene conversion and crossing over are lower than the true values, given that they are not equal to the true values.
E(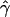 ) and E(
) and E(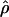 ) denote the mean of the estimates of gene-conversion and crossing-over rates.
) denote the mean of the estimates of gene-conversion and crossing-over rates.
V(γ) and V(ρ) denote the root mean square relative error for the estimates.
