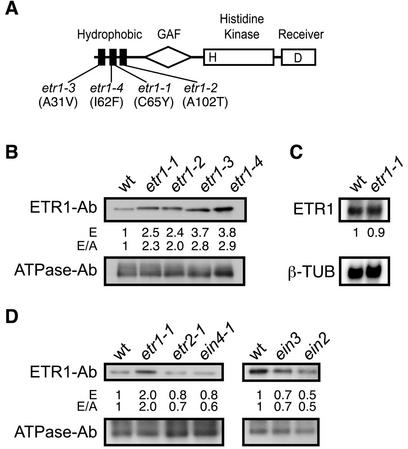
Figure 1.
Effect of ethylene-insensitive mutations upon expression of ETR1. A, Structure of ETR1 and position of ethylene-insensitive mutations. The hydrophobic ethylene-sensing domain, the GAF domain, the His kinase domain, and the receiver domain are indicated. The letters H and D indicate putative phosphorylation sites. B, Immunoblot analysis of wild-type and ethylene-insensitive mutants of ETR1. Etiolated seedlings were grown for 4 d, and the level of immunodetectable full-length receptor then determined from 10 μg of membrane proteins using an antibody directed against ETR1. Expression levels were quantified densitometrically (E) and also normalized against immunologically determined levels of the H+-ATPase (E/A) as an internal control. C, Northern-blot analysis of mRNA obtained from wild-type and etr1-1 seedlings. Blots were probed with an ETR1 probe and a β-tubulin gene probe as an internal control. The numbers represent the expression level of the ethylene receptor gene after normalization for the level of β-tubulin expression. D, Immunoblot analysis of ETR1 levels in additional ethylene-insensitive mutant backgrounds.