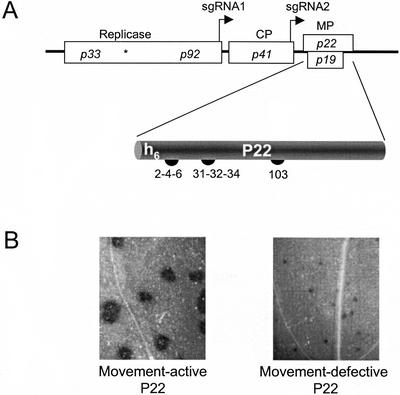
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the TBSV genome and features of P22 and its movement-defective mutants. A, The TBSV genome. Rectangles represent TBSV open reading frames (ORFs), and the asterisk (*) denotes the p33 amber stop codon to permit read-through translation of the other replicase gene, p92. The transcription initiation sites of two subgenomic RNAs (sgRNA1 and sgRNA2) are indicated by right-angled arrows. CP is the coat protein gene and MP denotes genes for two movement-associated proteins. The p22 ORF product P22 is denoted on the bottom with the position of six N-terminal His residues (h6). The numbers (2-4-6, 31-32-34, and 103) indicate positions of Glu and Asp residues substituted with Ala in the P22 movement-defective mutants used in this study (Chu et al., 1999). B, Comparison of cell-to-cell movement activity of wild-type P22 (left) versus a representative movement-defective P22 mutant (e.g. P22/103; right) using TBSV derivatives expressing the β-glucuronidase reporter gene substituted for the CP gene (Chu et al., 1999).