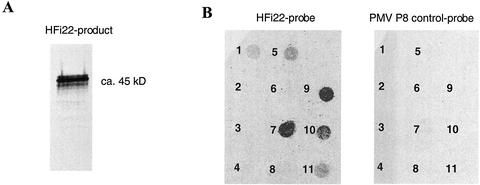
Figure 6.
Specific interaction of HFi22 with P22 in vitro. A, In vitro-translation product of HFi22 transcripts labeled with [35S]Met and mixed with NhisP22 was coimmunoprecipitated with P22-specific antibodies followed by SDS-PAGE and exposure of the dried gel to x-ray film. B, Overlay of [35S]Met-labeled HFi22-translation product onto nitrocellulose with 1-μg spots of the following proteins: 1, Rainbow molecular size markers (mix of myosin, phosphorylase b, bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin, carbonic anhydrase, trypsin inhibitor, and lysozyme; Amersham, Piscataway, NJ); 2, alkaline phosphatase; 3, ribonuclease; 4, bovine serum albumin; 5, lysozyme; 6, GST; 7, P22; 8, GST-P19; 9, P22/2-4-6; 10, P22/103; and 11, P22/31-32-34. The concentration of proteins present on the membrane was verified before and after loading (see text). No binding occurred with a control translation mix of 35S-labeled P8 of Panicum mosaic virus (Turina et al., 2000; right) or when an untranslatable HFi22 transcript was used to program the in vitro translation (data not shown).