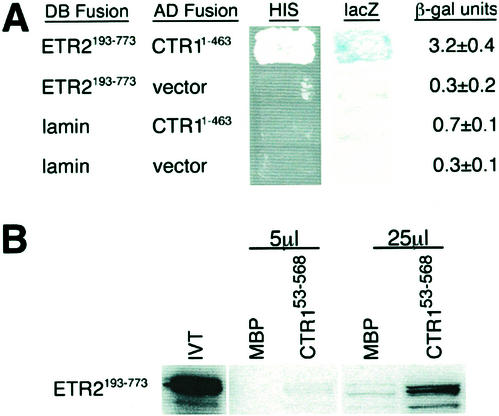
Figure 7.
ETR2 weakly interacts with CTR1's amino-terminal domain. A, The yeast two-hybrid assay was used to test whether ETR2 can interact with CTR1. A DB-ETR2293-738 fusion protein, representing the cytoplasmic portion of ETR2, was tested for its ability to associate with AD-CTR11-463, which represents the amino-terminal regulatory domain of CTR1. Interaction was assessed by activation of two reporter genes, including restoration of growth in the absence of exogenous His and β-galactosidase activity. For β-galactosidase activity, five transformants of each were measured and the average ± se is presented. B, An in vitro binding assay was used to confirm the association between ETR2 and CTR1. Either 5 or 25 μL of in vitro translated ETR2193-773, radiolabeled with [35S]Met, was associated with maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusions representing either MBP or MBP-CTR153-568. After several washes to remove unbound test protein, samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, fixed, soaked in a fluorographic reagent, and visualized by autoradiography.