Abstract
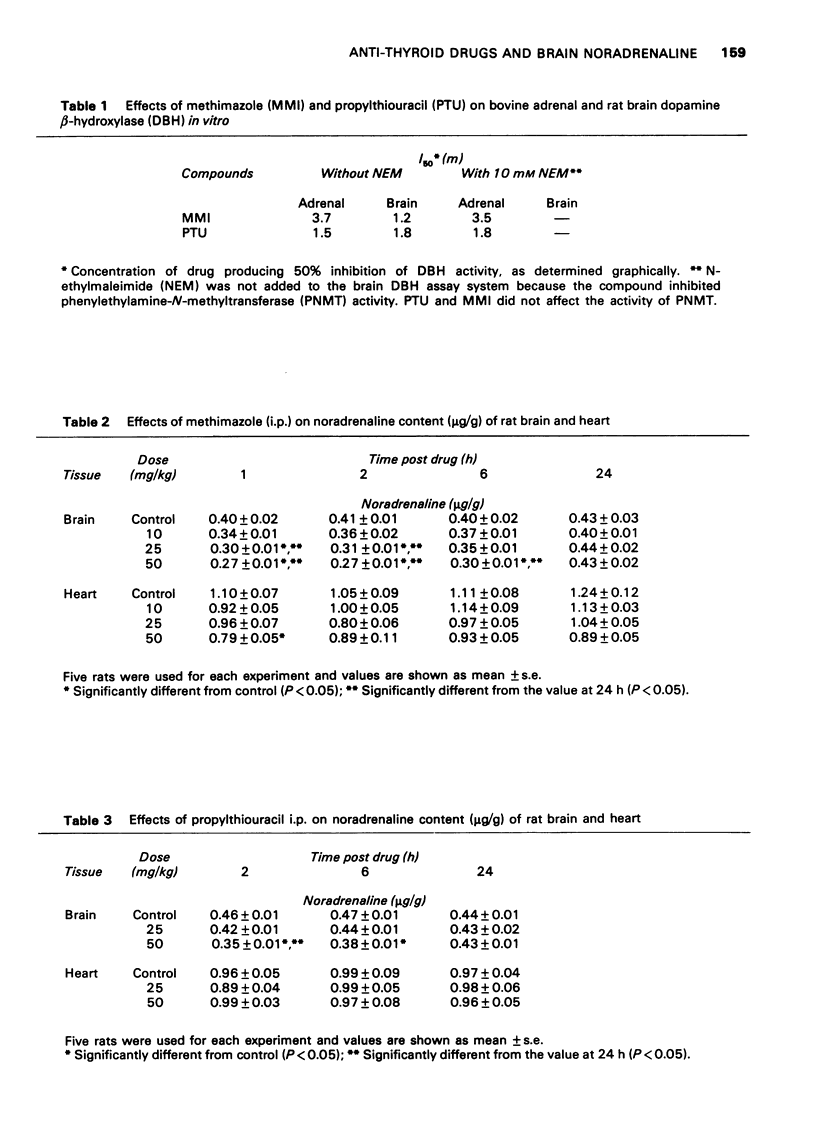
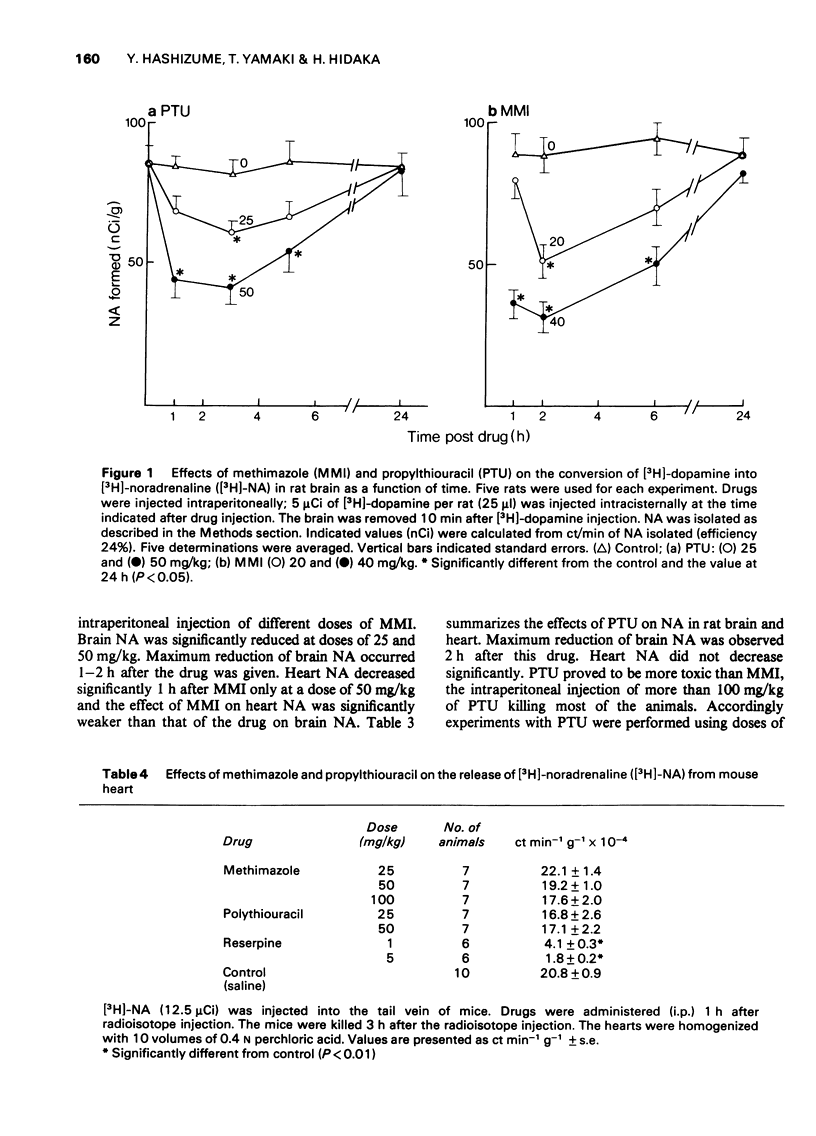
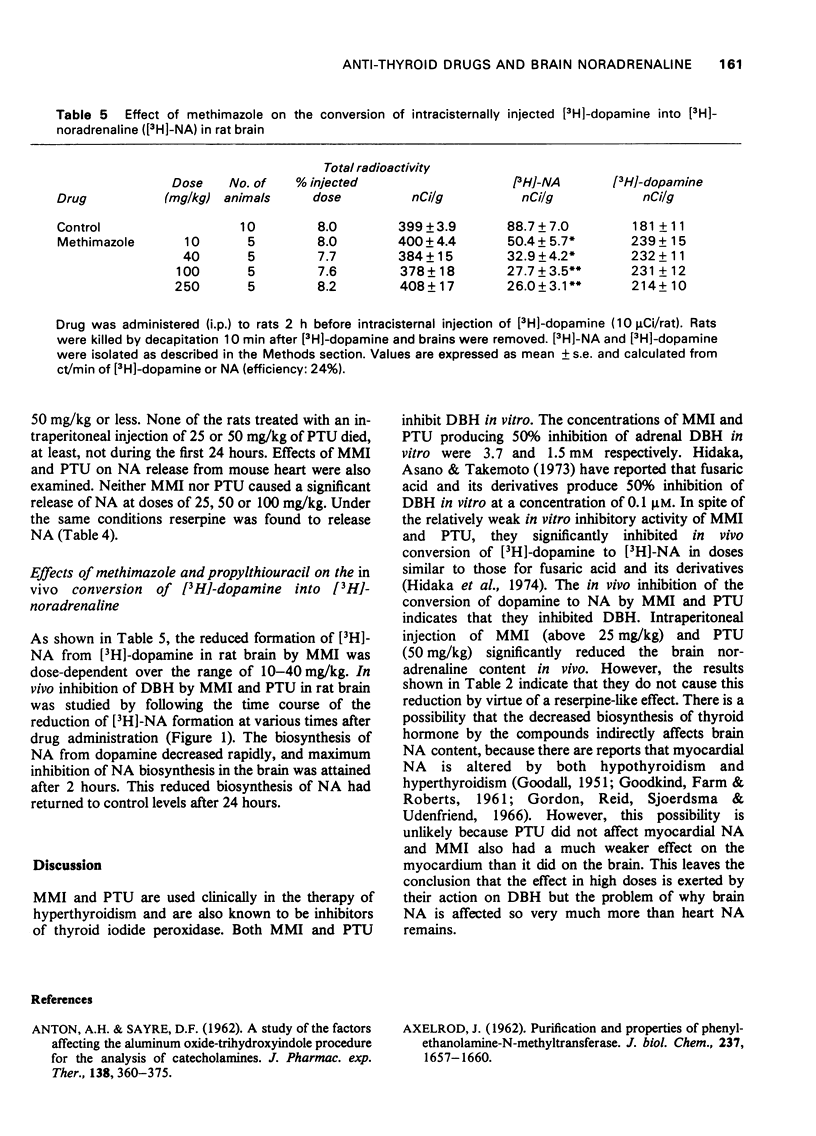
1 Methimazole (1-methyl-2-mercaptoimidazole, MMI) and propylthiouracil (6-propyl-2-thiouracil, PTU) which are used in the therapy of hyperthyroidism were found to reduce brain noradrenaline (NA) content. Endogenous NA levels in rat brain were reduced from 1 to 6 h after intraperitoneal injection of MMI by doses in excess of 25 mg/kg and by PTU at a dose of 50 mg/kg. However, endogenous NA in the rat heart was only slightly reduced after 50 mg/kg of MMI, and was not affected by PTU (50 mg/kg). 2 Both MMI and PTU effectively inhibited the in vivo conversion of [3H]-dopamine into [3H]-noradrenaline ([3H]-NA) in the brain of rats after a single intraperitoneal injection of doses above 10 mg/kg (MMI) and 25 mg/kg (PTU). This inhibition by MMI and PTU was dose-dependent over the range of 10 mg/kg to 50 mg/kg, was highest after 2-3 h and continued for at least 6 h after their injection; The conversion rates returned to normal after 24 hours. 3 The results suggest that the reduction of brain NA by these drugs is, at least in part, due to the inhibition of brain dopamine beta-hydroxylase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J. Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1657–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSSON A., WALDECK B. ON THE ROLE OF THE LIVER CATECHOL-O-METHYL TRANSFERASE IN THE METABOLISM OF CIRCULATING CATECHOLAMINES. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1963;20:47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1963.tb01718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREVELING C. R., DALY J. W., WITKOP B., UNDENFRIEND S. Substrates and inhibitors of dopamine-beta-oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Oct 8;64:125–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coval M. L., Taurog A. Purification and iodinating activity of hog thyroid peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5510–5523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Creveling C. R., Witkop B. The chemorelease of norepinephrine from mouse hearts. Structure-activity relationships. I. Sympathomimetic and related amines. J Med Chem. 1966 May;9(3):273–280. doi: 10.1021/jm00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S., Kaufman S. 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine beta-hydroxylase. Physical properties, copper content, and role of copper in the catalytic acttivity. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4763–4773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODKIND M. J., FRAM D. H., ROBERTS M. Effect of thyroid hormone on myocardial catecholamine content of the guinea pig. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1049–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R., Reid J. V., Sjoerdsma A., Udenfriend S. Increased synthesis of norepinephrine in the rat heart on electrical stimulation of the stellate ganglia. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Nov;2(6):610–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Asano T., Takemoto N. Analogues of fusaric (5-butylpicolinic) acid as potent inhibitors of dopamine -hydroxylase. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;9(2):172–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Hara F., Harada N., Hashizume Y., Yano M. Selective inhibition of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in the peripheral tissues by 5-dimethyldithiocarbamylpicolinic acid; its effect on stress-induced ulcer, ethanol-induced sleep and blood pressure. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Dec;191(3):384–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney C. P., Igo R. P. Studies of the biosynthesis of thyroxine. II. Solubilization and characterization of an iodide peroxidase from thyroid tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 7;113(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. A sensitive enzymatic assay for dopamine- -hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Sep;178(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatsu T., Kuzuya H., Hidaka H. Inhibition of dopamine beta-hydroxylase by sulfhydryl compounds and the nature of the natural inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jul 11;139(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


