Abstract
1 When cat spleen slices were exposed to a potassium-enriched (140 mM) Krebs solution, 367 +/- 31 ng g-1 5 min-1 of noradrenaline (NA) was released into the bathing medium. 2 Phenylephrine and clonidine (10(-7) to 10(-3) M) did not significantly modify the potassium-evoked NA release; acetylcholine decreased it in a dose-dependent manner. 3 Phenoxybenzamine increased NA release by 50% but phentolamine did not alter it; high concentrations of this drug greatly decreased NA release. Cocaine increased the NA release by about 30%. 4 It is suggested that the failure of sympathomimetic amines to depress, and of alpha-adrenoceptor blocking agents to enhance the release of NA by high potassium concentrations may be related to prolonged depolarization of the nerve terminals, which may desensitize presynaptic alpha-receptors. The fact that the same drugs are able to modify NA release during electrical nerve stimulation may be ascribed to the much shorter periods of depolarization occurring under these conditions.
Full text
PDF
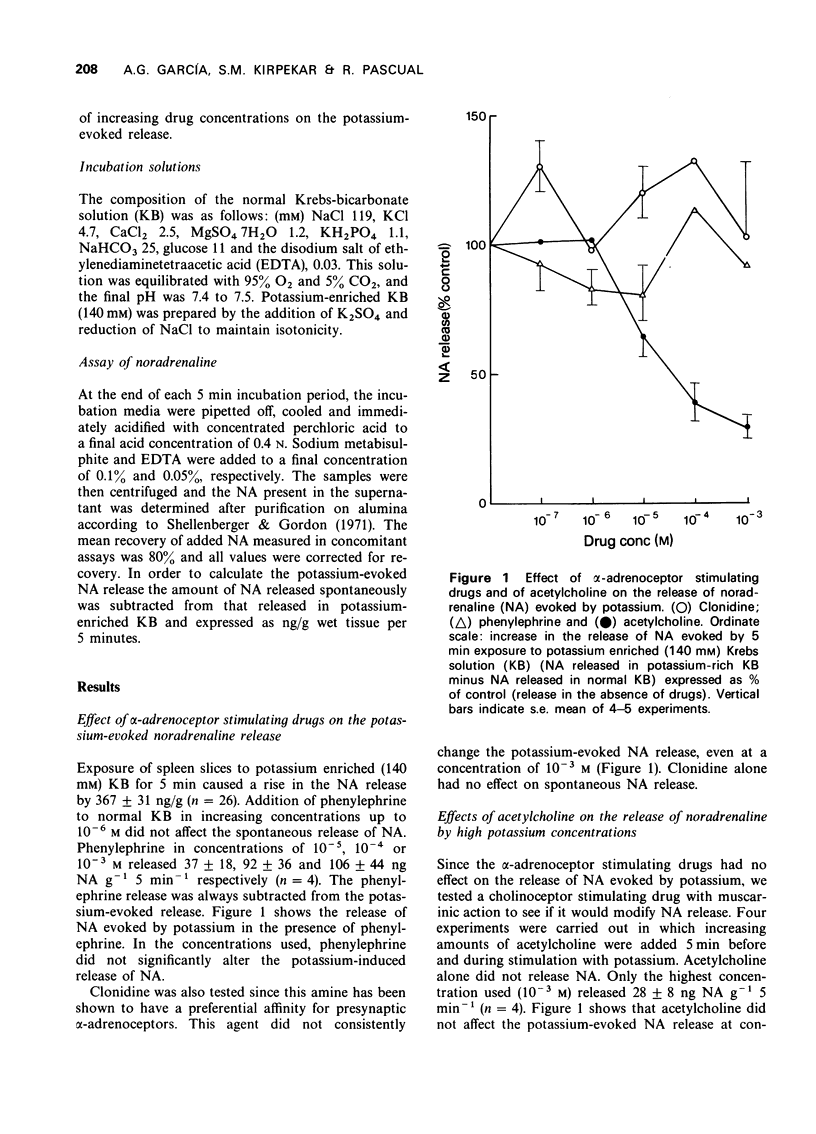
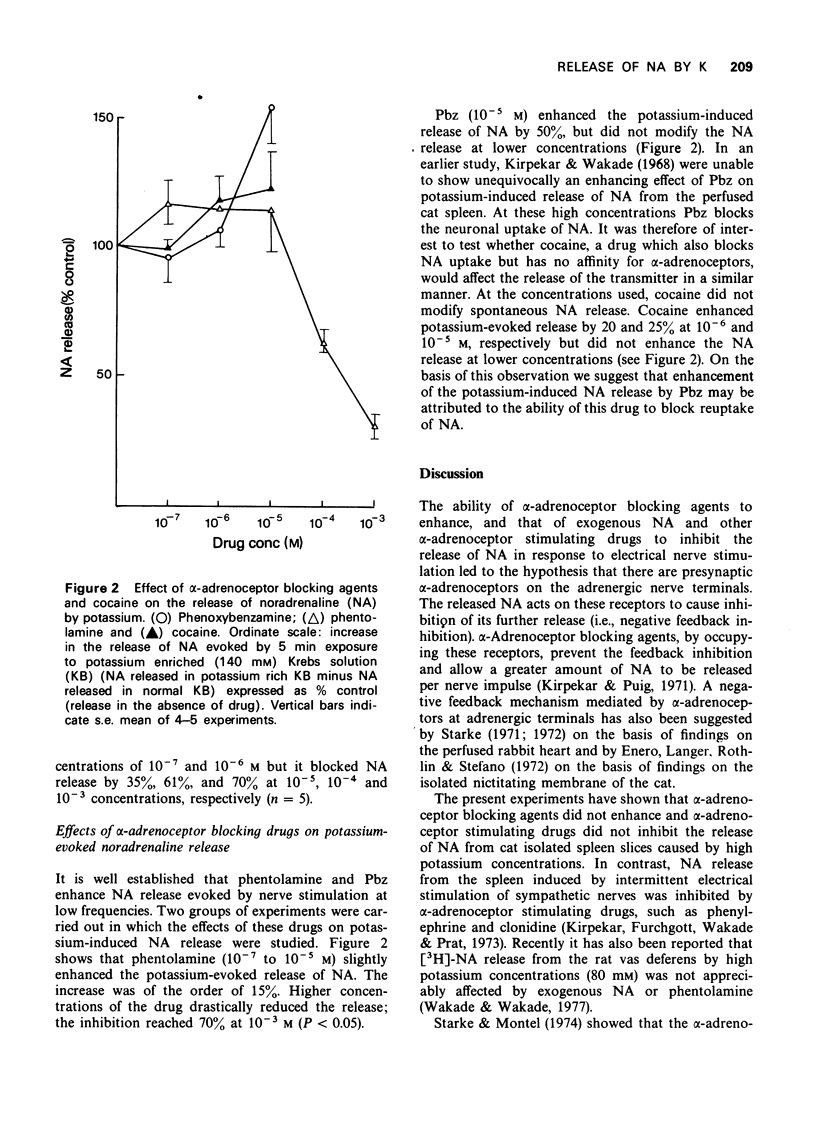


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubey M. P., Muscholl E., Pfeiffer A. Muscarinic inhibition of potassium-induced noradrenaline release and its dependence on the calcium concentration. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00510816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enero M. A., Langer S. Z., Rothlin R. P., Stefano F. J. Role of the -adrenoceptor in regulating noradrenaline overflow by nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;44(4):672–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLESPIE J. S., KIRPEKAR S. M. THE INACTIVATION OF INFUSED NORADRENALINE BY THE CAT SPLEEN. J Physiol. 1965 Jan;176:205–227. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. G., Kirpekar S. M., Sanchez-Garcia P. Release of noradrenaline from the cat spleen by nerve stimulation and potassium. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):301–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idowu O. A., Zar M. A. Inhibitory effect of clonidine on a peripheral adrenergic synapse [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;58(2):278P–278P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Furchgott R. F., Wakade A. R., Prat J. C. Inhibition by sympathomimetic amines of the release of norepinephrine evoked by nerve stimulation in the cat spleen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Dec;187(3):529–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Wakade A. R. Effect of calcium on the relationship between frequency of stimulation and release of noradrenaline from the perfused spleen of the cat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;287(2):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00510451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Puig M. Effect of flow-stop on noradrenaline release from normal spleens and spleens treated with cocaine, phentolamine or phenoxybenzamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):359–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Wakade A. R. Release of noradrenaline from the cat spleen by potassium. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(3):595–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellenberger M. K., Gordon J. H. A rapid, simplified procedure for simultaneous assay of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine from discrete brain areas. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):356–372. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha sympathomimetic inhibition of adrenergic and cholinergic transmission in the rabbit heart. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(1):18–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00501004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Altmann K. P. Inhibition of adrenergic neurotransmission by clonidine: an action on prejunctional -receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1973 Apr;12(4):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(73)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Endo T., Taube H. D. Relative pre- and postsynaptic potencies of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;291(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00510821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Influence of -receptor stimulants on noradrenaline release. Naturwissenschaften. 1971 Aug;58(8):420–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00591535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Montel H., Gayk W., Merker R. Comparison of the effects of clonidine on pre- and postsynaptic adrenoceptors in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Alpha-sympathomimetic inhibition of Neurogenic vasoconstriction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;285(2):133–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00501149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Montel H. Influence of drugs with affinity for alpha-adrenoceptors on noradrenaline release by potassium, tyramine and dimethylphenylpiperazinium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;27(3):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K., Taube H. D., Browski E. Presynaptic receptor systems in catacholamingergic transmission. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Feb 15;26(4):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


