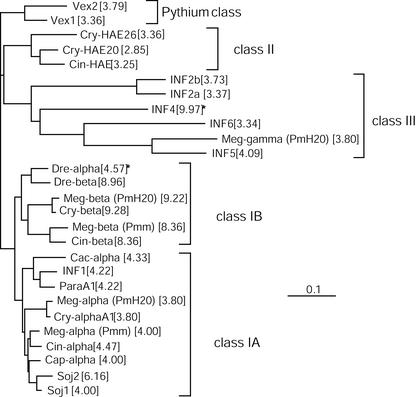
Figure 4.
Phylogeny of the elicitin family from Phytophthora spp. and Pythium vexans. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method based on the mature protein sequences shown in Figure 3. The length of the branches reflects weighted amino acid substitutions and the scale bar represents 10% weighted sequence divergence. Vex1 and Vex2 were used as out groups. The calculated pI for each protein is indicated between square brackets. The five classes representing main clusters of the tree are indicated. The stars indicate proteins that may belong to another class, because two of the criteria defining an elicitin class are the pI and the occurrence of a C-terminal tail after the 98-amino acid-long elicitin domain. Thus, Dre-α would belong to class I-A and Inf4 to class I-B although Inf4 disclose a signal peptide sequence of class III elicitin (see Table III).