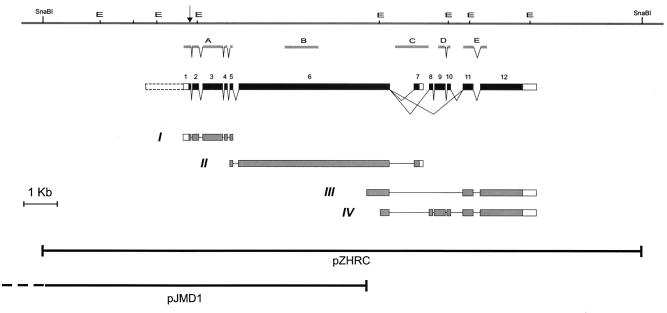
Figure 1.
A physical and transcription map of the mud gene. The horizontal line at the top represents the genomic DNA; the centromere is to the right. Restriction sites for EcoRI (E) and SnaBI enzymes are indicated. The position of the codon that is changed in mud4 is indicated by an arrow. Below the genomic DNA is diagrammed the exon-intron structure of the mud transcription unit, as derived from the analysis of various cDNAs isolated by PCR (line I, clone AP-C) or from libraries (line II, clone RZ15; line III, clone LD24364; line IV, clone LD31911). Filled boxes represent potential coding regions and open boxes correspond to untranslated sequences. The dashed open box indicates a noncoding upstream portion for the mud transcription unit that is predicted by fgenesh, but corresponding cDNAs have not yet been found. For each splice variant, only the longest isolated cDNA is diagrammed. Complete sequences for these clones have been deposited, lines I and II as GenBank accession no. AF209068 and lines III and IV as GenBank accession no. AF174134. The sequences show that two versions of exon 12 are used: exon 12a (for cDNA III) having its 5′ end 12 nt upstream of the 5′ end of exon 12b (for cDNAIV). Below the cDNAs are shown the inserts of two partially overlapping genomic constructs that respectively succeed and fail to rescue mud phenotypes: pZHRC and pJMD1 (which extends 4.4 kb distally, as indicated by the dashed line). Between the genomic and exon-intron maps are shown the positions of probes A-E, used for Northern blot analyses.