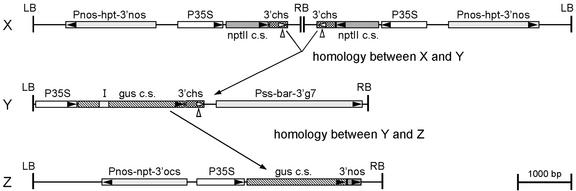
Figure 1.
Schematic outline of the T-DNA constructs (drawn to scale), present in silenced locus X, recombinant gene Y, and target gene Z (T-DNAs of pGVCHS287, pGUSchsS, and pXD610, respectively), and of the transcript homology between X, Y, and Z. The structure of locus X and Y is indicated; locus Z contains two or more copies of the XD610 T-DNA. Δ, 3′chs polyadenylation signal; 3′chs, 3′-UTR of the chalcone synthase gene of snapdragon (Anthirrinum majus); 3′g7, 3′-UTR of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens octopine T-DNA gene 7; 3′nos, 3′-UTR of the nopaline synthase gene; 3′ocs, 3′-UTR of the octopine synthase gene; bar, bialaphos acetyltransferase-coding sequence conferring phosphinothricin resistance; gus c.s., GUS-coding sequence; hpt, hygromycin phosphotransferase-coding sequence; I, artificial intron; LB, left T-DNA border; nptII c.s., neomycin phosphotransferase II-coding sequence; P35S, CaMV 35S promoter; Pnos, nopaline synthase promoter; Pss, promoter of the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase; RB, right T-DNA border.