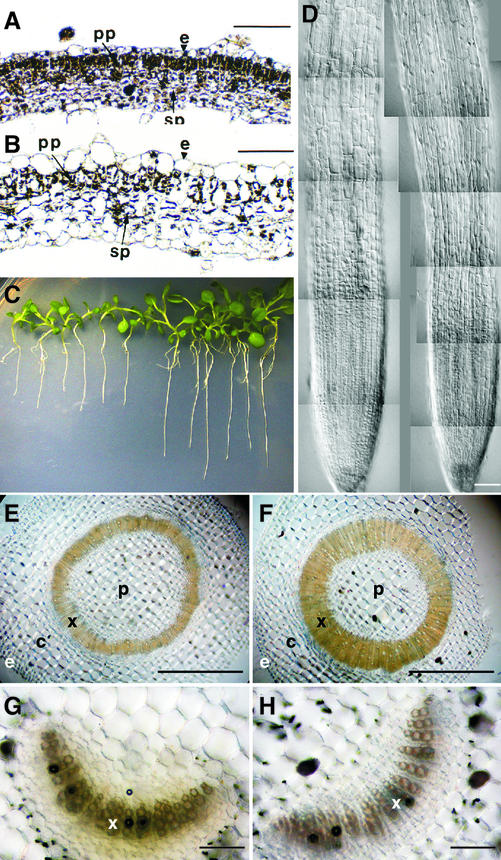
Figure 7.
Anatomical features of transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the GmEXP1 gene. A and B, Cross sections of leaves of wild-type and transgenic plants, respectively. Leaf cells of the transgenic plants are enlarged and irregularly layered, reflecting ectopic expression of the GmEXP1 gene in the transgenic tobacco plants. e, Epidermis; pp, palisade parenchyma; sp, spongy parenchyma. C, Transgenic tobacco seedlings of line S1 in the T2 generation overexpressing the GmEXP1 cDNA under the obstacle-touching condition. After vernalization, the seedlings were incubated on 1.5% (w/v) agar plates in an inclined position (45°) for 17 d after germination. The seedlings on the left side are wild-type tobacco plants, and the ones on the right are transgenic. D, Comparison of the root apical region in a wild-type control tobacco plant (left) and a transgenic plant (right). The cells in the transgenic plant are more elongated than those of the wild-type control plant. Bar in D = 100 μm. E and F, Cross sections of stems of wild-type control plants (E) and the transgenic plants (F) at the same developmental stage. Bars in E and F = 1,000 μm. c, Cortex; e, epidermis; p, pith; x, xylem. G and H, Cross sections of petioles of wild-type control plants (G) and the transgenic plants (H) at the same developmental stage. Bars in G and H = 100 μm. x, Xylem.