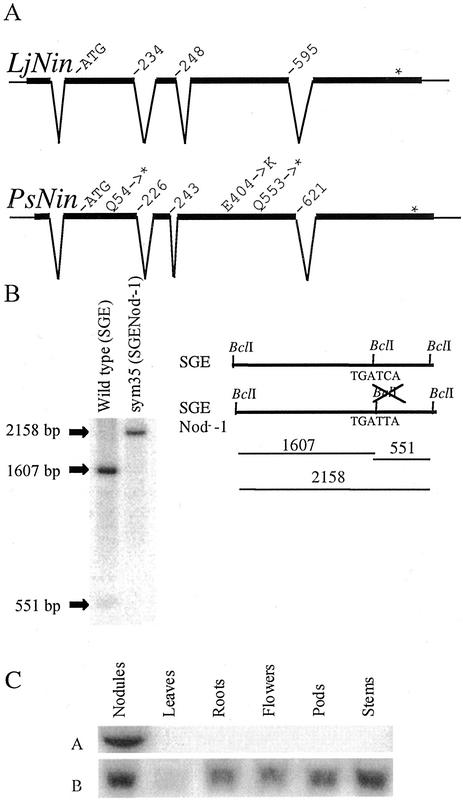
Figure 2.
The intron-exon structure of LjNin and PsNin genes is conserved. A, The sequences of Sym35 from pea cv Finale and L. japonicus were compared with their respective cDNAs and aligned. Apart from short stretches in the promoter regions (Fig. 5), the genomic sequences show little or no similarity outside of the exons. Amino acid positions at the exon-intron boundaries and the changes in sym35 mutant alleles are indicated. B, Southern hybridization visualizing the RFLP generated by mutation of a BclI restriction site in the sym35 SGENod−-1 allele. Positions of the BclI sites in the mutant and wild-type alleles and the fragments generated by BclI digestion of genomic DNA are shown in the schematic drawing. The hybridization probe used covers 2 kb of the coding sequence. C, Northern analysis of PsNin expression in various pea organs. A visualizes the hybridization with the Sym35-specific probe. B shows the control hybridization with ubiquitin.