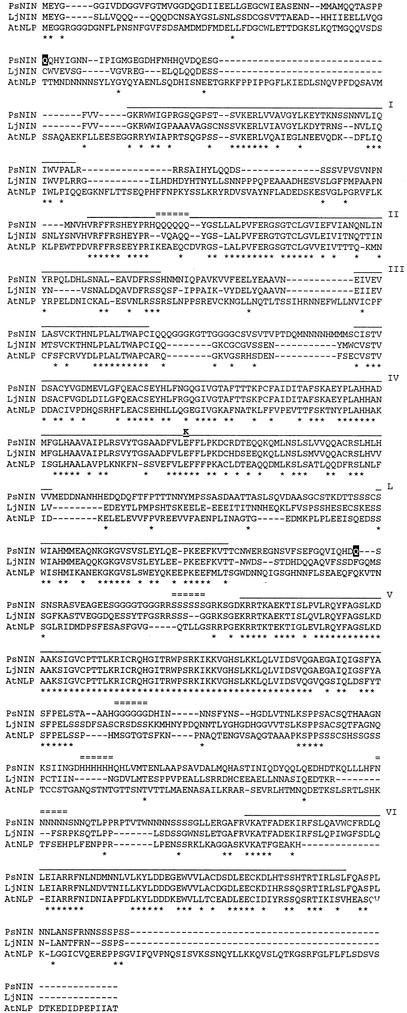
Figure 3.
Identification of conserved domains in LjNIN and PsNIN. The translation products of LjNin and PsNin cDNAs are aligned with the most homologous NLP from Arabidopsis using ClustalX. For assignment of protein domains, an alignment including all nine NLPs from Arabidopsis was carried out, but only the sequence of the most homologous NLP from Arabidopsis is shown in the figure. Six regions of high conservation between all 11 proteins are shown (domains I–VI) together with one region (L) conserved between LjNIN, PsNIN, and the most homologous NLP from Arabidopsis. Region V is the most conserved region and surrounds the putative DNA binding and dimerization, RWP-RK, motif. Region VI has similarity to the PB1 heterodimerization domain conserved in animals, fungi, and plants. Domains I to VI and L are overlined and identical amino acids marked by asterisks. Positions of stop codons (aa in black shadow) or amino acid changes caused by the three sym35 mutations are indicated in the PsNIN sequence. The small tracts of repeated amino acids are marked by double lines.