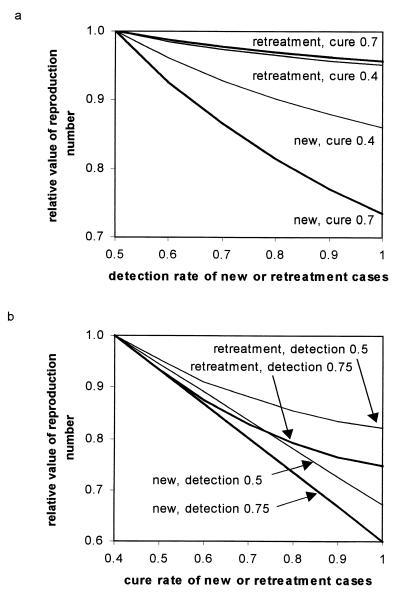
Figure 3.
Interactions between case detection and cure rates in the control of MDR-TB. Initial values of the reproduction number, Rθm, have been scaled to 1 on the vertical axis to aid comparison of different strategies. Horizontal axes explore the impact of improving case detection (a) and cure rates (b). In a, Rθm is more effectively reduced by improving the case detection rate of new cases rather than of retreatment cases (previous failures). The impact of detecting and treating new cases is greater when the cure rate is higher (thick lines), and so is the relative advantage of treating new cases over retreatment cases (bigger gap between thick lines than between thin lines). In b, Rθm is more effectively reduced by improving the cure rate of new cases rather than of retreatment cases. The impact is greater when the detection rate is higher (0.75 instead of 0.5), and this applies to both new and retreatment cases (same gap between thick lines as between thin lines).