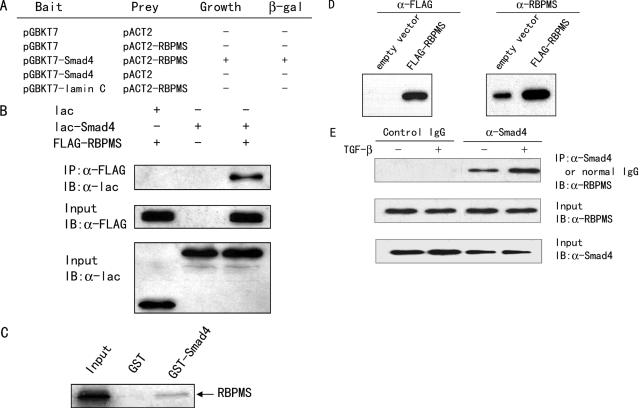
Figure 1.
RBPMS interacts with Smad4 in yeast, in mammalian cells and in vitro. (A) Identification of RBPMS as a Smad4-interacting protein by the yeast two-hybrid assay. Yeast AH109 cells were transformed with different plasmids and grown on SD/−Trp−Leu−His−Ade. +, grown within 96 h; −, no growth within 96 h. Positive colonies were tested for β-galactosidase activity. +, turned blue within 2 h; −, did not turn blue within 2 h. (B) Interaction of RBPMS with Smad4 in mammalian cells. 293T cells, cultured in regular medium, were transfected with expression plasmids as indicated. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using anti-FLAG monoclonal antibody (Sigma-Aldrich), and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-lac polyclonal antibody (Stratagene). (C) Interaction of RBPMS with Smad4 in vitro. Glutathione–Sepharose beads bound with GST-Smad4 or with GST were incubated with 35S-labeled RBPMS. After washing the beads, the bound proteins were eluted and subjected to SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. (D) Characterization of anti-RBPMS mouse antiserum by immunoblotting. The lysates from 293T cells transfected with FLAG-RBPMS or its empty vector were prepared and the proteins detected with anti-FLAG (left panel) or anti-RBPMS (right panel) antibody. (E) Interaction of endogenous RBPMS with Smad4 in vivo. 293T cells, cultured in serum-free medium, were treated without and with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 1 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with either anti-Smad4 antibody or preimmune control serum (Santa Cruz). The precipitates were analyzed by immunoblot using anti-RBPMS.