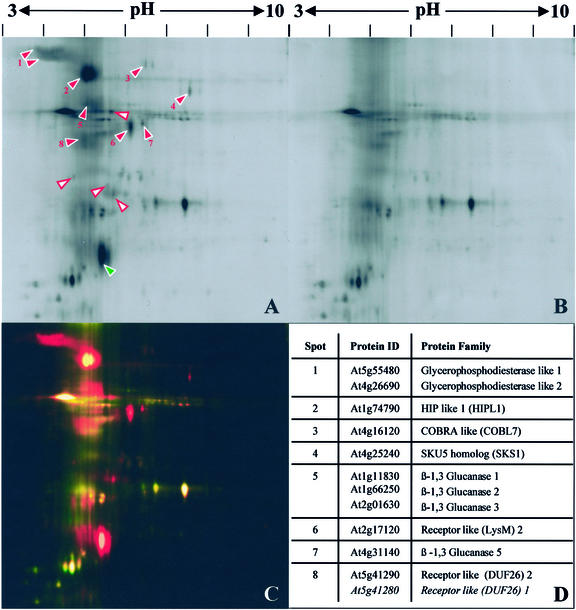
Figure 1.
Identification of Arabidopsis GAPs sensitive to Pi-specific phospholipase C. Integral membrane proteins from callus were prepared by TX-114 phase partitioning and treated with Pi-PLC or buffer only (control). After repartitioning, proteins released into the aqueous phases were labeled with CyDyes. The samples were mixed and then separated by electrophoresis in a single two-dimensional gel. Gels were imaged with a fluorescence scanner. A to D, Broad pH range (3–10). A, Aqueous phase after Pi-PLC treatment. B, Control aqueous phase. C, False-color overlay of Pi-PLC-treated (red) and control (green) fractions. D, LC-MS/MS identifications of GAPs. Numbers correspond to red arrowheads in A. Some spots contained mixtures of related proteins. E to H, Narrow pH range (4–7). E, Aqueous phase after Pi-PLC treatment. F, Control aqueous phase. G, False-color overlay of Pi-PLC-treated (red) and control (green) fractions. H, LC-MS/MS identifications of GAPs. Numbers correspond to red arrowheads in E. Arrowheads in A and E indicate spots specifically enriched in the Pi-PLC-treated fractions. Red, numbered arrowheads correspond to identified GAPs (D and H). White arrowheads with red borders indicate unidentified Pi-PLC-sensitive proteins. Green arrowheads correspond to Pi-PLC-derived proteins.