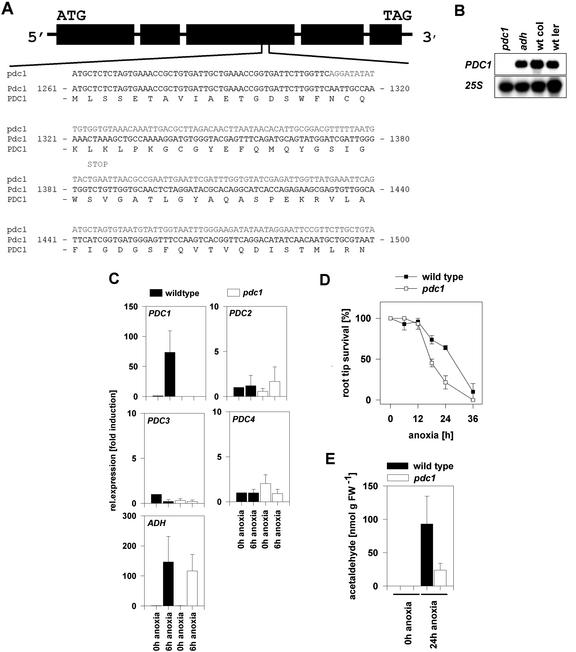
Figure 4.
Interference of a T-DNA insertion in PDC1 with gene expression and survival under anoxia. A, Structure of the Arabidopsis PDC1 gene. DNA sequences of the wild type and the mutant line showing the T-DNA-derived sequences in bold and the wild-type amino acid sequence. A potential stop codon in the reading frame of the T-DNA insertion in PDC1 is indicated. B, Expression level in pdc1 and adh seedlings treated for 6 h under anoxia. Total RNA (10 μg) from wild-type seedlings of the accessions Col-0 and Ler and from pdc1 (Col-0) and adh (Ler) were subjected to RNA gel-blot analysis with a specific probe from the 3′-untranslated region of PDC1. 25S labeling indicated equal RNA loading. C, Quantification of mRNA levels of PDC and ADH genes in wt and pdc1 mutant seedlings under normoxia (0-h anoxia) or after 6-h anoxia. Expression levels were normalized with respect to the internal control ACT2 and are plotted relative to the expression at 0-h anoxia. Data bars represent the mean ± se level of transcripts from three experiments with independent RNA extractions. D, Survival of pdc1 and wt seedlings under anoxia. The survival of the existing root tip was scored from seedlings subjected to different periods of anoxia and a 3-d-long recovering time. Black squares represent wild-type seedlings; white squares represent mutant seedlings. Data represent the average of three survival experiments with independent plant material ± se. E, Production of acetaldehyde in roots submitted to 24-h anoxia measured by gas chromatography. Detached roots were infiltrated with 50 mm Glc and 0.1 mm CaSO4 and were incubated for 24 h in an anoxic bench or in normal atmosphere. Values represent the average of between three and five measurements of different populations of seedlings ± se.