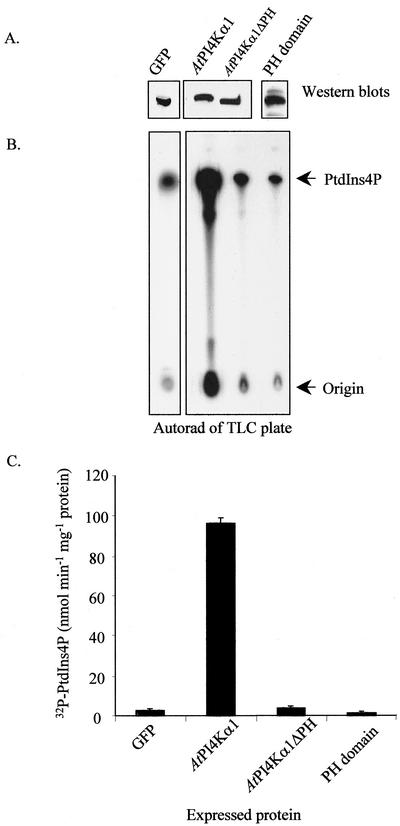
Figure 6.
The PH domain is essential for efficient PtdIns 4-kinase activity. Sf9 insect cells were infected with recombinant baculoviruses harboring the cDNAs for cytosolic green fluorescent protein (GFP), AtPI4Kα1, AtPI4Kα1ΔPH, and the AtPI4Kα1 PH domain alone. Three days after infection, the cells were harvested, lysed, and 8 μg of the cleared lysates was assayed for PtdIns 4-kinase activity in the presence of added substrate, PtdIns, and [γ-32P]ATP. A western blot probed with anti-AtPI4Kα1 or anti-GFP identifying the expressed recombinant polypeptides is shown at the top of A. Below the western is the resulting autoradiograph of the thin-layer chromatography (TLC) plate used to separate the 32P-labeled lipid products of the PtdIns 4-kinase assay. B, Quantification of the TLC plate shown in A using a Bioscan Imaging Scanner. Shown are the averages of duplicate samples of a representative experiment. Similar results were obtained from at least four independent recombinant baculovirus infections.