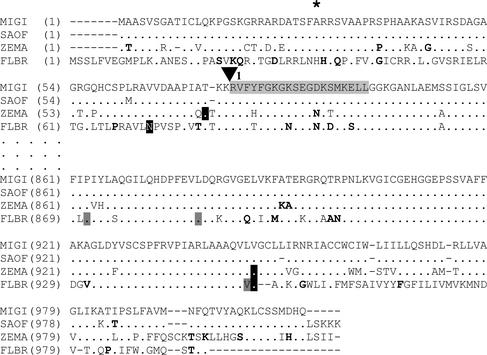
Figure 5.
Partial putative protein sequence comparison of chloroplastic C4-PPDK from M. × giganteus (MIGI), sugarcane (SAOF), maize (ZEMA), and F. brownii (FLBR). Protein sequences were deduced by translation of cDNA: GenBank accession numbers AY262272 (MIGI), AF194026 (SAOF), J03901 (ZEMA), and U08399 (SAOF). Vertical ellipsis marks represent a break in the pictured sequence. Gaps in sequence alignment are indicated by a dash. Residues identical and similar to M. × giganteus are indicated by dots or bolding, respectively. ▾, The splice acceptor site for the first intron in C4-PPDK, as determined by homology with maize. The asterisk identifies the amino acid position at which C4ppdkMg1 and C4ppdkMg2 differ in the region picture. The region of deletion in C4ppdkMg3 is indicated by black text on a light gray background. The N terminus and C terminus of ZEMA (Matsuoka, 1995) and FLBR (Usami et al., 1995) are indicated by white text on a black background. Note that FLBR is a C3/C4 intermediate dicot with a PPDK that is reported to be cold stable (Usami et al., 1995), whereas the remaining species are C4 grasses. The three residues reported to be responsible for conferring cold tolerance to FLBR PPDK (Ohta et al., 1996) are indicated by black text on a dark gray background.