Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To examine whether sodium pump activity plays a part in the pathogenesis of thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. DESIGN--Measurement of platelet sodium-potassium ATPase and in vivo sodium pump activities in healthy subjects and thyrotoxic subjects with and without paralysis. SETTING--University hospital in Hong Kong. SUBJECTS--21 healthy subjects, 23 untreated thyrotoxic subjects, 13 untreated men with periodic paralysis, seven treated thyrotoxic subjects, and six treated men with periodic paralysis. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Platelet Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity and plasma rubidium concentration after oral loading. RESULTS--Median (range) platelet Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity in thyrotoxic subjects was 253 (169-821) mumol inorganic phosphate/h/g protein--significantly higher than that in healthy subjects (134 (81-180) mumol/h/g protein; p less than 0.001). Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity in those with periodic paralysis was 374 (195-1196) mumol/h/g protein, again significantly higher than that in healthy subjects (p less than 0.001) and that in other thyrotoxic subjects (p less than 0.01) despite similar degrees of hyperthyroidism. Activities in treated thyrotoxic subjects with and without periodic paralysis were 148 (110-234) and 131 (86-173) mumol/h/g protein respectively. Mean (95% confidence interval) plasma rubidium concentration five hours after oral administration in thyrotoxic subjects (7.0 (6.6 to 7.5) mumol/l) was significantly lower than in healthy subjects (10.2 (9.5 to 10.9) mumol/l; p less than 0.001) and higher than in those with periodic paralysis (6.0 (5.7 to 6.3) mumol/l; p less than 0.01). CONCLUSIONS--Sodium pump activity in untreated subjects with periodic paralysis is higher than in other thyrotoxic subjects, and this may be responsible for the hypokalaemia.
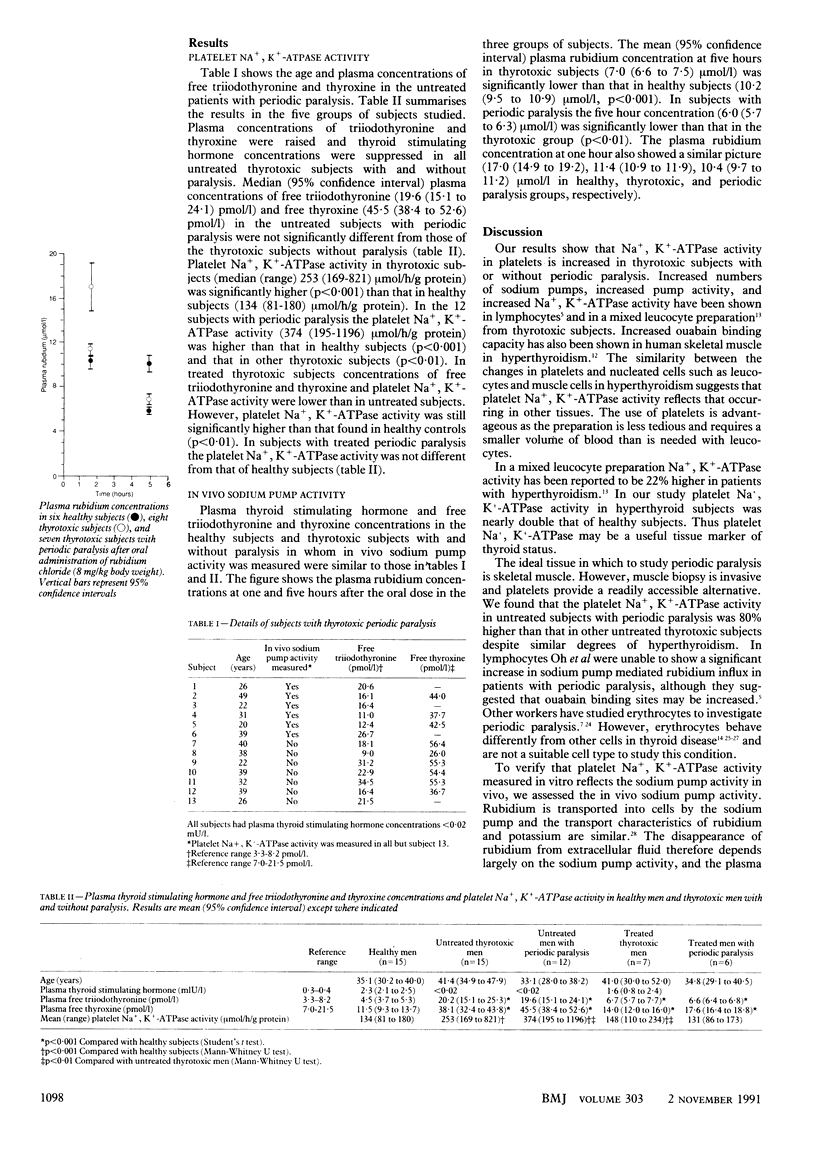
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott R. D., White R., Jerums G. Effect of thyroid status on ouabain binding to the human lymphocyte. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jun;54(6):1150–1156. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-6-1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumanayagam M., MacDonald D., Cockram C. S., Swaminathan R. Erythrocyte sodium fluxes, ouabain binding sites, and Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity in hyperthyroidism. Metabolism. 1990 Sep;39(9):952–957. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumanayagam M., MacDonald D., Cockram C. S., Swaminathan R. The effect of hyperthyroidism on in vivo aging of erythrocyte ouabain-binding sites and intracellular sodium and potassium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Jul;71(1):260–263. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-1-260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano Y., Liberman U. A., Edelman I. S. Thyroid thermogenesis. Relationships between Na+-dependent respiration and Na+ + K+-adenosine triphosphatase activity in rat skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):368–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI108288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron D. N., Khan F. A. Optimal conditions for measurement of Na+,K+-ATPase activity of human leucocytes. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Feb;68(2):143–149. doi: 10.1042/cs0680143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J. C., Israel Y. Active transport of Rb86 in human red cells and rat brain slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Aug;174(2):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon N. A., Aronson J. K., Hallis K. F., White N. J., Raine A. E., Grahame-Smith D. G. A method for the study of cation transport in vivo: effects of digoxin administration and of chronic renal failure on the disposition of an oral load of rubidium chloride. Clin Sci (Lond) 1984 May;66(5):569–574. doi: 10.1042/cs0660569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. A., Ertingshausen G. Direct method for determining inorganic phosphate in serum with the "CentrifiChem". Clin Chem. 1972 Mar;18(3):263–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Neuromuscular manifestations of Graves' disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1972 Dec;47(12):919–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieve R. R., Meltzer H. L., Taylor R. M. Rubidium chloride ingestion by volunteer subjects: initial experience. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;20(4):307–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00403562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber R. S., Loeb J. N. Early enhancement of passive potassium efflux from rat liver by thyroid hormone: relation to induction of Na,K-ATPase. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):291–297. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallis K. F., Boon N. A., Perkins C. M., Aronson J. K., Grahame-Smith D. G. A sensitive high-temperature electrothermal atomic absorption analysis for Rb+ in erythrocytes and plasma of normal and hypertensive persons. Clin Chem. 1985 Feb;31(2):274–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins B. R., Ma J. T., Lam K. S., Wang C. C., Yeung R. T. Association of HLA antigens with thyrotoxic Graves' disease and periodic paralysis in Hong Kong Chinese. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Sep;23(3):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan F. A., Baron D. N. Ion flux and Na+,K+-ATPase activity of erythrocytes and leucocytes in thyroid disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Feb;72(2):171–179. doi: 10.1042/cs0720171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen K., Nørgaard A., Gøtzsche C. O., Thomassen A., Clausen T. Effect of thyroid function on number of Na-K pumps in human skeletal muscle. Lancet. 1984 Jul 7;2(8393):8–10. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91996-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Yeung R. T., Benson E. A., Wang C. Erythrocyte sodium-potassium pump in thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Aust N Z J Med. 1989 Feb;19(1):6–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1989.tb01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. H., Akera T. Increased (Na+,K+)-ATPase concentrations in various tissues of rats caused by thyroid hormone treatment. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):723–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx A., Ruppersberg J. P., Pietrzyk C., Rüdel R. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis and the sodium/potassium pump. Muscle Nerve. 1989 Oct;12(10):810–815. doi: 10.1002/mus.880121005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadzean A. J., Yeung R. Periodic paralysis complicating thyrotoxicosis in Chinese. Br Med J. 1967 Feb 25;1(5538):451–455. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5538.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKINAKA S., SHIZUME K., IINO S., WATANABE A., IRIE M., NOGUCHI A., KUMA S., KUMA K., ITO T. The association of periodic paralysis and hyperthyroidism in Japan. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Dec;17(12):1454–1459. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-12-1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh V. M., Taylor E. A., Yeo S. H., Lee K. O. Cation transport across lymphocyte plasma membranes in euthyroid and thyrotoxic men with and without hypokalaemic periodic paralysis. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Feb;78(2):199–206. doi: 10.1042/cs0780199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubython E. J., Cumberbatch M., Morgan D. B. Changes in the number and activity of sodium pumps in erythrocytes from patients with hyperthyroidism. Clin Sci (Lond) 1983 Apr;64(4):441–447. doi: 10.1042/cs0640441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shizume K., Shishiba Y., Sakuma M., Yamauchi H., Nakao K., Okinaka S. Studies on electrolyte metabolism in idiopathic and thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. I. Arteriovenous differences of electrolytes during induced paralysis. Metabolism. 1966 Feb;15(2):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turaihi K., Khokher M. A., Barradas M. A., Mikhailidis D. P., Dandona P. 86Rb(K) influx and [3H]ouabain binding by human platelets: evidence for beta-adrenergic stimulation of Na-K ATPase activity. Metabolism. 1989 Aug;38(8):773–776. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo P. P., Chan S. H., Lui K. F., Wee G. B., Lim P., Cheah J. S. HLA and thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 30;2(6142):930–930. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6142.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung R. T., Tse T. F. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis. Effect of propranolol. Am J Med. 1974 Oct;57(4):584–590. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


