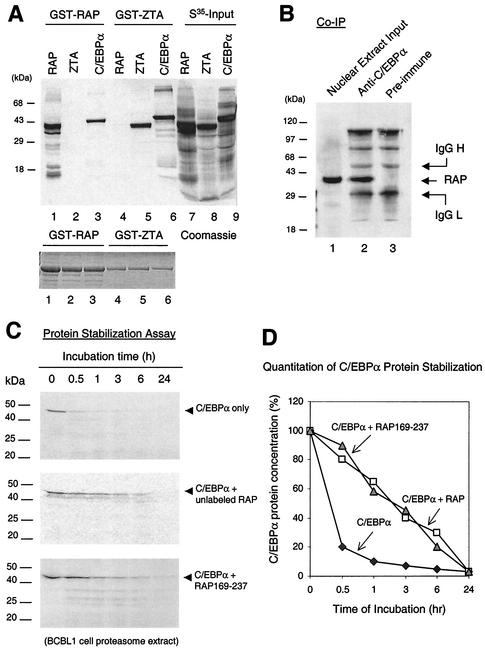
FIG. 1.
KSHV RAP interacts with and stabilizes C/EBPα (A) In vitro GST affinity assay. (Upper panel) Lane 1, [35S]RAP binding to GST-RAP (self-interaction); 2, lack of [35S]ZTA binding to GST-RAP; 3, strong [35S]C/EBPα binding to GST-RAP; 3 and 4, binding of [35S]ZTA but not [35S]RAP to GST-ZTA; 5, strong binding of [35S]C/EBPα to GST-ZTA; 6 to 9, input [35S]-labeled in vitro-translated KSHV RAP, EBV ZTA, and C/EBPα. (Lower panel), Coomassie staining of the GST, GST-RAP, and GST-ZTA fusion proteins used. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of RAP with C/EBPα from KSHV-positive BCBL-1 cells undergoing the KSHV lytic cycle after TPA induction. Detection was done by Western immunoblotting with anti-RAP PAb. Lanes: 1, positive control of RAP in the input cell lysate (10% of input sample); 2, recovery of RAP by immunoprecipitation using anti-C/EBPα PAb; 3, negative control, immunoprecipitation with preimmune goat serum failed to recover RAP. (C) In vitro protein stability assay using a BCBL-1 proteasome extract. (Top panel) Time course showing that the half-life of [35S]C/EBPα incubated alone was 30 min. (Middle) Parallel time course showing that preincubation of [35S]C/EBPα with unlabeled RAP increased the half-life of C/EBPα from 30 min to 3 h. (Bottom) Parallel time course showing that preincubation of [35S]C/EBPα with mutant RAP(169-237) also increased the half-life of C/EBPα to 3 h. (D) Graph showing quantitatively measured C/EBPα protein levels plotted against proteasome incubation time. IgG, immunoglobulin G.