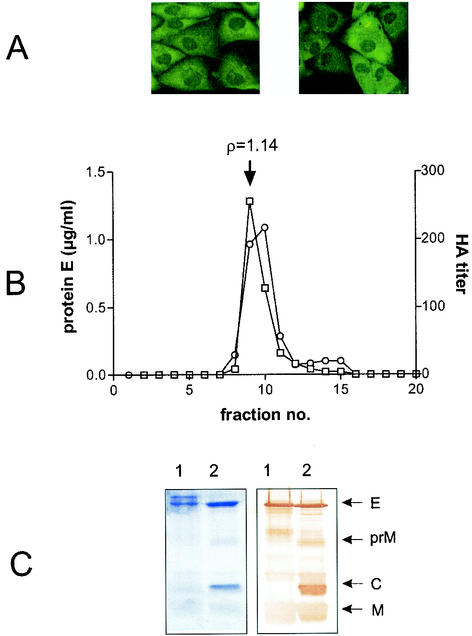
FIG. 4.
Characterization of CHO-ME cells and released particles. (A) Cell morphology and protein E expression of low-passage cells (left) and after 15 passages (right) as examined by immunofluorescence. (B) Determination of buoyant density of secreted particles. Particles were precipitated from supernatants of CHO-ME cells purified by rate zonal centrifugation and then subjected to sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Individual fractions were tested for their protein E content by SDS-ELISA (open circles) and the presence of hemagglutination activity (open boxes). The buoyant density, as determined for the peak fraction, is indicated above the graph. (C) Protein analysis of purified particles by fractionation on a 15% denaturing polyacrylamide gel. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie blue staining (left) or immunoblot analysis (right). 1, CHO-ME derived particles; 2, wild-type virus. The positions of viral structural proteins are indicated on the right.