FIG. 2.
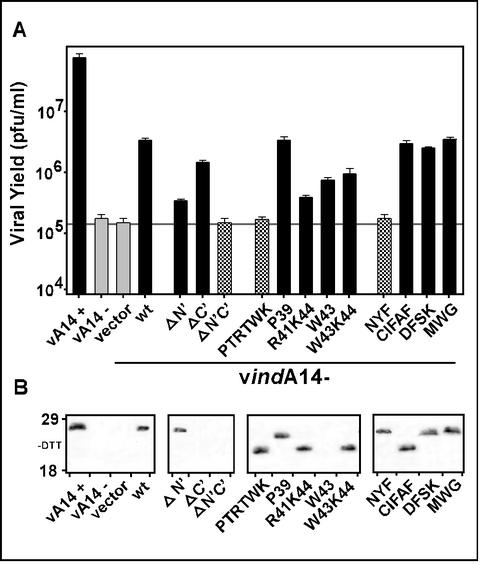
Transient rescue of vindA14 performed with structural mutants of A14. (A) Determination of complementation competency by titration of viral yield from infections and transfections. BSC40 cells were infected at an MOI of 5 with vindA14 virus. Infections were performed in the presence (+) or absence (−) of TET, followed by transfection of 10 μg of empty vector or vector encoding the indicated alleles of A14. Extracts were harvested at 24 hpi and were titrated in order to assess the ability of the various A14 alleles to substitute for endogenous virus A14 in a transient-rescue assay. Cells infected in the presence (+) and absence (−) of TET served as positive and negative controls, respectively; cells infected in the absence of inducer and transfected with empty vector or with the plasmid encoding wt A14 served as the benchmarks for transient rescue. The horizontal grey line shows the titer obtained upon transfection of empty vector. The data shown represent the average of three independent experiments. (B) Immunoblot analysis of A14 expression. Aliquots of the extracts described above were resolved by nonreducing SDS-17% PAGE and were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-A14 serum to monitor A14 expression from the endogenous and transfected alleles. The positions of the 18,000- and 29,000-Mr standards are shown at the left.