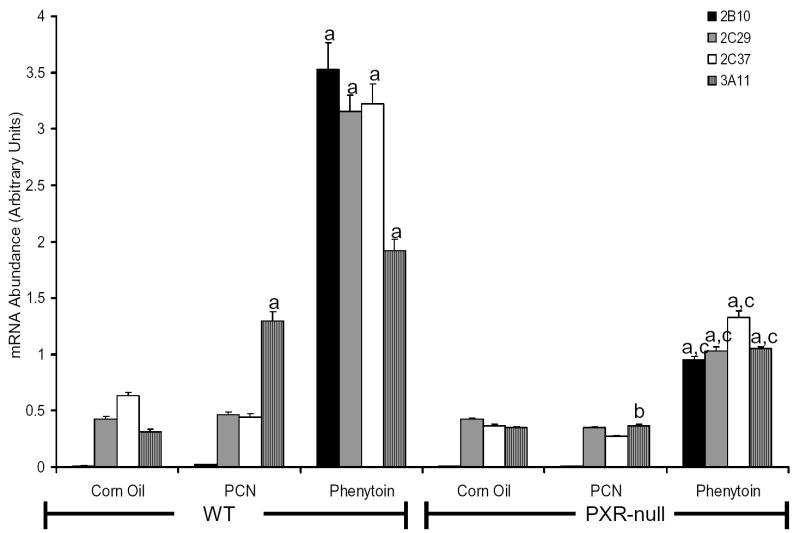
Figure 7.
Evaluation of Cyp2c37 induction by phenytoin and PCN in PXR-null mice. Mice were treated with phenytoin as described above. Mice treated with PCN (80 mg/kg) were treated orally for three consecutive days. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to evaluate target gene mRNA content in response to PCN and phenytoin. Target genes were normalized to a reference gene, β-actin. CYP2B10, CYP2C29, and CYP2C37 mRNA induction by phenytoin was reduced, not abolished in PXR-null mice. CYP3A11 mRNA was induced by PCN in congenic wild-type mice, but was eliminated in PXR-null mice. In contrast, induction of CYP3A11 mRNA by phenytoin was reduced, not abolished in PXR-null mice. Values expressed above represent the relative abundance of gene specific mRNA +/− SE. P-values were determined using the Tukey-Kramer HSD Test. a p< 0.05, significantly higher than corn oil controls. b p < 0.05, significantly lower than wild-type treated with PCN. c p < 0.05, significantly lower than wild-type treated with phenytoin.